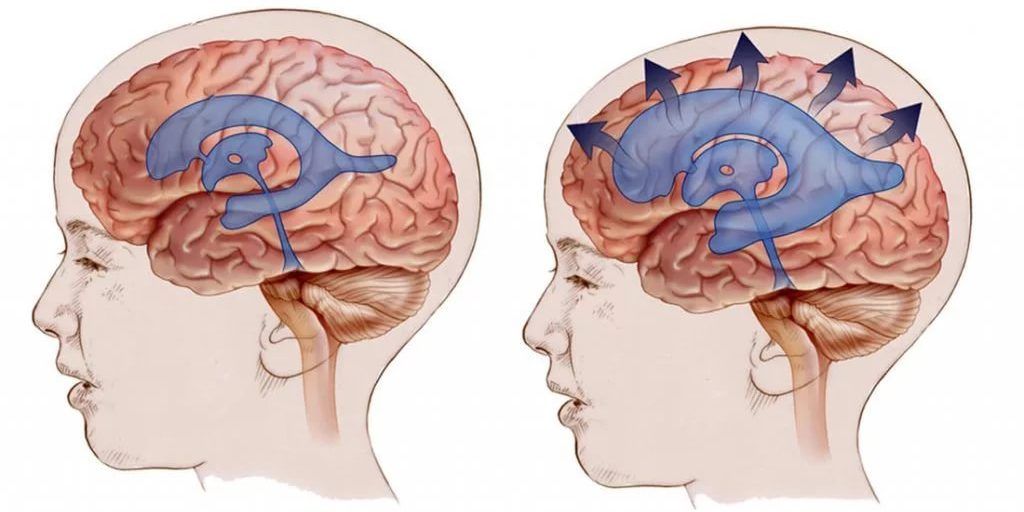
Causes of headaches
Headache is one of the most common symptoms accompanying various neurological, somatic and mental diseases. Today, about 300 causes of its occurrence are identified.
Types of headaches
Traditionally, headaches are divided into:
- Primary – headache as an independent disease.
- Secondary or symptomatic – headache as a symptom of another disease.
Headache classification
Primary pain
- Migraine ;
- Tension headache ;
- Cluster headache and other trigeminal autonomic cephalgias;
- Other forms of primary headache (e.g., associated with physical or sexual exertion, cough headache, hypnic headache, thunderclap headache, etc.).
Symptomatic pain
- associated with head and/or neck injury;
- associated with vascular lesions of the skull and cervical spine;
- associated with nonvascular intracranial lesions;
- associated with various substances or their withdrawal (including drug-induced (abuse) GB associated with excessive use of analgesics or triplans);
- associated with infections;
- associated with a violation of homeostasis (including hypertension associated with arterial hypertension);
- facial pain associated with disorders of the structures of the skull, neck (including cervicogenic), eyes (including those associated with glaucoma), ears, nasal cavity, sinuses (including those associated with sinusitis), teeth, oral cavity or other structures of the skull and face (including GB associated with temporomandibular joint dysfunction);
- associated with mental illness.
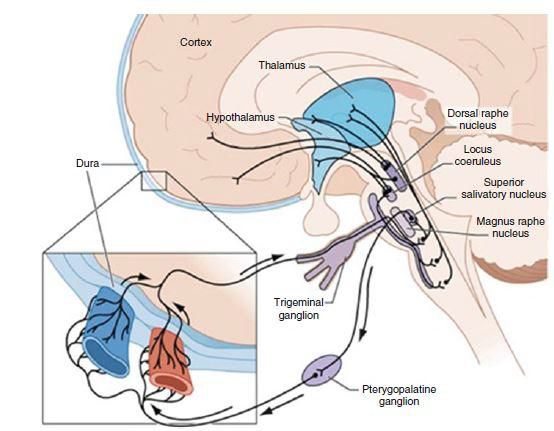
Cranial neuropathies and other pain
- Painful cranial neuropathies and other facial pain;
- Other forms of headache.
Secondary (symptomatic) headache
A headache that accompanies another causative disease is called secondary (symptomatic).
This type of pain is characterized by:
- associated with the onset or exacerbation of the underlying disease,
- disappears with successful treatment of the underlying disease
Primary headache is much more common than secondary headache.
“Danger Signals”
Often, symptomatic headache is a symptom of an organic disease with an unfavorable prognosis. To detect it, it is necessary to pay attention to the so-called “danger signals”.
The danger signals (“RED FLAGS”) are:
- The occurrence of headaches is associated with physical exertion, coughing, and sexual activity.
- The appearance of a new, atypical headache
- Headache that progressively worsens
- The appearance of neurological symptoms (impaired consciousness, memory loss, etc.)
- Presence of focal neurological symptoms or systemic disease (fever, joint pain, etc.)
- Headache onset after age 50
- Any abnormalities on neurological and/or general somatic examination.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 23.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: