Radiofrequency denervation
The technique of radiofrequency denervation (termination of nerve impulse conduction) is modern, reliable, and quite convenient for both the doctor and the patient.
Radiofrequency denervation is one of the most accurate medical technologies, based on the selective thermal destruction of clearly defined nerve structures by special electrodes when a high-frequency electric current passes through them.
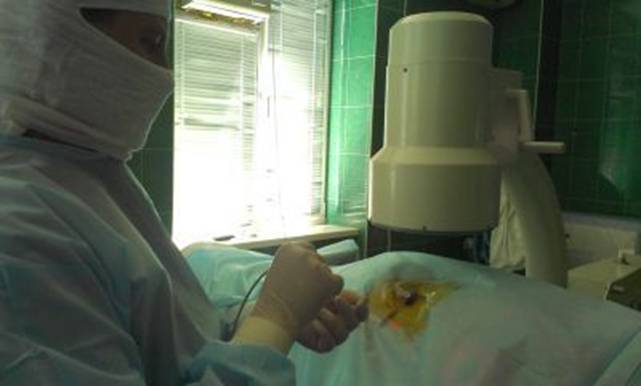
An electrode (thin wire) connected to a radiofrequency generator is guided through a special channel (hollow needle) under the control of an X-ray machine to the desired area of the body where the source of the pain impulses is located.
Next, electrical stimulation (sensory and motor) is performed to prevent damage to important nerve structures.
Only after this is the actual RFA performed, during which a high-frequency electric current passes through the body’s tissues, selectively heating them, resulting in a blockade of nerve impulses from the fibers located right near the electrode. Thus, after the manipulation, the pain disappears.
Radiofrequency denervation has significant advantages over other methods of treating chronic pain. It does not require general anesthesia, tissue incision, is performed under local anesthesia, can be performed on an outpatient basis, the total duration of the intervention is 20-30 minutes, and the analgesic effect lasts from 6 months to 2 years or more, and complications are very rare, and the possibility of repeated manipulation remains if necessary.
Radiofrequency ablation can be successfully used for such manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis as facet syndrome and discogenic pain.
Facet syndrome
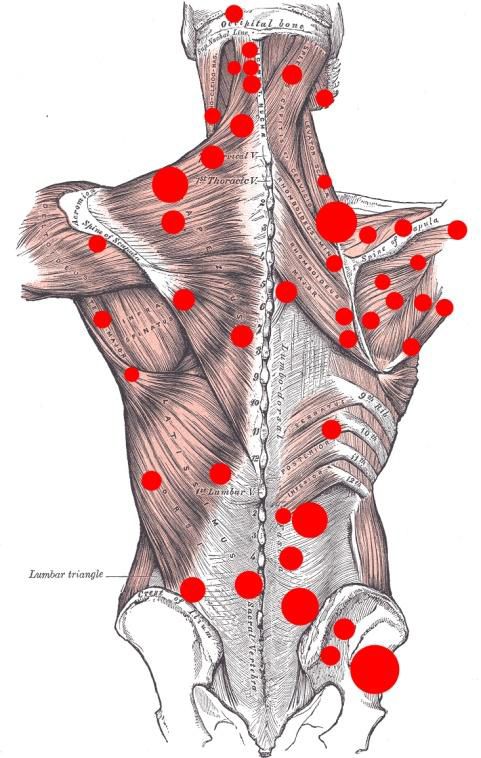
Pain that occurs with pathological changes in the joints of the spine (facet joints ) is a fairly common type of pain in the neck and back. The causes of “facet syndrome” can be inflammation of these joints, osteochondrosis, scoliosis (curvature of the spine), and the consequences of repeated spinal injuries .
Pain in facet syndrome has its own characteristics.
- it occurs or intensifies when the body is tilted back and to the sides,
- weak, but sometimes radiates to the legs and usually not below the knee, worsens at night,
- as well as with monotonous postures, often found during sedentary work, this pain is relieved when active habitual movements are resumed, “unloading” the spine;
- Morning “stiffness” of the spine is also characteristic.
Discogenic pain
Pain originating from the intervertebral discs is also a very common problem. This pain is characterized by the fact that it occurs in an upright position of the body and with active movements in the spine.
Surgery is usually not indicated unless there is a herniated disc or spinal nerve root compression. However, discogenic pain can be quite severe and debilitating, which impairs the quality of life of patients.
These “mechanical” back pain types are usually not treated with surgical methods, and conservative treatment is ineffective. Radiofrequency ablation effectively denervates the facet joints and intervertebral discs, providing high-quality pain relief for up to a year or more.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 22.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: