Spinal fractures and injuries
Spinal fractures are classified as severe skeletal trauma. Every year in Ukraine, spinal cord injury occurs in 2,000-3,000 victims. About 76% of patients become disabled of groups I-II.
Main reasons
- Road accident
- fall from a height
- diving into water
- strokes of various etiologies
- Osteoporosis is a disease in which minor physical exertion (a bad turn, a jump, a fall) is enough to cause a fracture.
- metastatic lesion of the spine.
Often, a fracture of bone structures is combined with damage to soft tissues:
- connection,
- disks,
- nerve roots
- spinal cord.
Classification of fractures
Spinal fractures are:
- stable (when the spine remains stable despite the injury, i.e. does not shift relative to its axis)
- unstable (when the spine shifts from its axis, resulting in various neurological symptoms),
- isolated (without damage, and with spinal cord damage)
- also distinguish compression fractures,
- fractures of the wives,
- explosive fractures,
- compression-explosion fractures.
Depending on the type of spinal fracture and associated injuries, the clinical picture and complaints will differ. Complaints depend on the localization and area of damage to the spine and nervous structures.
Clinical picture
- Lack of movement below the level of injury (plegia)
- Loss of sensation below the level of injury (hypo-anesthesia)
- Central type pelvic organ dysfunction in the form of acute retention or incontinence.
- Pain in the area of injury
Statistics
Patients with severe lesions that result in complete conduction disturbances in the spinal cord have only a 5% chance of full recovery.
- If complete paralysis persists for 72 hours after injury, the probability of recovery is 0%.
- If minimal sensitivity is maintained, the patient has a 50% chance of recovery.
- 10-20% of patients do not survive to be hospitalized.
- 3% die during the evacuation and hospitalization phase.
Causes of death
The leading cause of death among trauma survivors:
- pneumonia,
- thromboembolism
- and sepsis.
Diagnostics
- X-ray (allows you to determine the condition of the bones).
- MRI allows you to determine the degree of trauma to the spinal cord and intervertebral disc, and in metastatic lesions of the spine, to determine the degree of tumor growth.
- The leading diagnostic method is multispiral computed tomography (MSCT) – with this method of examination, it is possible to examine in detail the condition of the bone structures of the spine, the condition of the spinal cord, detect hematomas and foreign bodies, assess the degree of spinal cord compression, and conduct dynamic observation.
Treatment
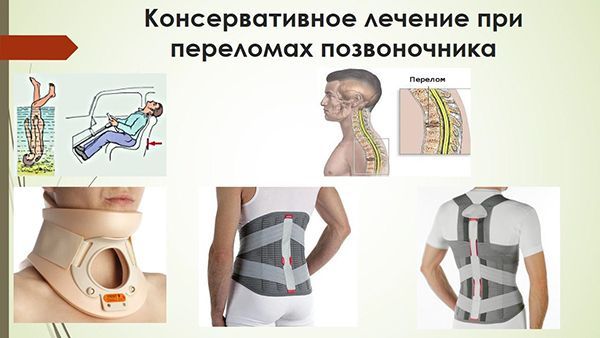
Conservative treatment for “stable” fractures consists of fixing the damaged part of the spine.
Surgical treatment is performed for unstable spinal injuries.
- In case of burst fractures, fracture-dislocations, and compression-burst fractures, a reconstructive decompression-stabilizing surgery is performed aimed at freeing the spinal cord from compressing fragments and restoring the axis of the spinal column.
- In case of compression fractures due to osteoporosis and small metastases to the vertebral body, kyphoplasty or vertebroplasty is performed .
The neurosurgical department provides all types of treatment for spinal fractures at any time from the moment of injury. Surgical interventions are performed at any level of the spine, of any complexity. Reconstructive operations are also performed for chronic post-traumatic deformities.
Conservative treatment of spinal fracture
Reasons
The spine is not only the support and foundation of the entire body, but also an important communication system, consisting of 32-34 vertebrae, which are interconnected by a huge number of tendons, joints and muscles.
Despite its strength, as a result:
- falling from a height,
- traffic accident,
- diving, shooting
- and mine and blast injuries,
A vertebral fracture may occur.
Vidi
Fractures are:
- cervical (in case of accidents and jumping into water)
- and lumbar (when falling from a height) sections of the spine.
The most dangerous consequence of spinal fractures is spinal cord trauma (impact or damage), which can impair or completely eliminate the functions of the lower extremities (movement and/or sensitivity in the extremities, dysfunction of the pelvic organs).
Surgical treatment
In case of vertebral fractures, it is indicated in case of instability of the damaged sections (loss of the supporting function of the spine), or in case of neurological deficits after injury (impaired movements, sensitivity, delay/incontinence of stool and urination), which occurs as a result of compression of the spinal cord by damaged vertebrae, their fragments or foreign bodies.
In the absence of neurological disorders and with preservation of the integrity of the vertebral body, surgical treatment is not indicated. In such cases, immobilization of the damaged spine for a period of up to 3 months is prescribed:
- In case of cervical vertebrae fractures, a Philadelphia collar is applied,
- with vertebral fractures in the thoracic region
- and lumbar regions, immobilization is performed with rigid corsets.
Pain relief therapy
In addition, the patient is prescribed painkillers, because such injuries are accompanied by severe pain symptoms, calcium preparations, and physical therapy. A patient with a spinal injury should be taken to a specialized neurosurgical hospital as soon as possible, because only a neurosurgeon can make the right decision about the tactics of patient management.
In the neurosurgical department, not only is a decision made about further treatment tactics based on modern European and American protocols, but also the selection of adequate corrective corsets from German manufacturers is carried out.
Surgical treatment of spinal fractures
The main indications for surgical intervention are:
- the presence of unstable damage or the threat of instability,
- fractures complicated by spinal cord injury,
- lack of effect from conservative treatment.
Target
The objectives of surgical treatment of spinal fractures are:
- elimination of compression of the spinal cord and/or roots,
- elimination of spinal deformity ,
- reliable fixation of damaged vertebrae.
Surgical intervention prevents the worsening of neurological disorders and allows rehabilitation treatment to begin as early as possible .
Today, there are many methods of surgical interventions on the spine, which depend on the level of the affected area and the number of damaged vertebrae.
Types of interventions
Surgical interventions are:
- Open – in which a skin incision and massive mobilization of soft tissues are performed, the advantage of this technique is maximum visualization and thorough revision of damaged areas, but the access is quite traumatic, which significantly complicates the postoperative course with pronounced pain syndrome and increases the risk of complications.
- The surgery can also be performed using a minimally invasive method – thanks to special tools, the stabilizing structure is installed using small skin punctures, through which titanium screws are inserted under constant X-ray control. This technique minimizes tissue trauma, facilitates the postoperative period, and allows rehabilitation treatment to begin earlier.
The neurosurgical department performs all types of surgical interventions on the spine and spinal cord:
- the most modern spinal stabilization techniques have been implemented ,
- availability of special tools,
- Modern intraoperative X-ray equipment allows for high-level surgical interventions.
Rehabilitation period
In the post-operative ward, the patient receives comprehensive rehabilitation treatment:
- Exercise therapy,
- massage,
- physiotherapy.
Neurosurgeon Zhuravlev A.F.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 22.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: