Infectious brain lesions
Brain infections are serious infectious diseases that can lead to death. The brain controls many different functions in the body, such as movement, coordination, perception, thinking, and more. Infections can damage these functions and lead to significant health problems.
The main infections of the brain include:
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms include headache , fever, seizures, nausea, and vomiting.
- Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain. Symptoms include headache, fever, disorientation, fatigue, and others.
- A brain abscess is an infection or collection of pus in the brain. Symptoms include headache, fever, seizures, fatigue, and more.
- Poliomyelitis is an inflammation of the spinal cord that can lead to paralysis. Symptoms include headache, fever, seizures, fatigue, and more.
- Herpes is a viral infection that can affect the brain. Symptoms include headache, fever, skin rash, seizures, and more.
Treatment for brain infections involves the use of antibiotics, antivirals, and/or other medications that can help reduce inflammation and combat symptoms. However, it is important to remember that treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Neuroinfections are among the most dangerous for human life and health. Normally, the brain and spinal cord have reliable protection against the penetration of infectious agents. Unlike other organs, in them each capillary is surrounded by an additional “case” of protective cells – the so-called neuroglia cells. These cells create a reliable barrier for many microorganisms and toxins, as well as medicinal substances.
Under certain conditions, for example:
- decreased immunity,
- head and spine injuries,
- prolonged septic infections
The blood-brain barrier breaks down and pathogens enter the CNS. Infectious inflammation of its membranes (meningitis) or the brain substance itself (encephalitis) occurs.
The causes of meningoencephalitis can be:
- bacteria,
- viruses,
- mushrooms,
- parasites.
Microorganisms can enter the brain after trauma to its membranes, fractures of the bones of the skull or base of the skull, in the presence of cerebrospinal fluid , after neurosurgical operations, and in septic conditions on the background of immunodeficiencies.
Infectious lesions of the spinal cord
Infectious spinal cord lesions occur as a result of infectious diseases that enter the spinal canal through the bloodstream or lymphatics or directly through the tissues of the spinal cord. Such infections can be bacterial, viral, or fungal.
Typically, an inflammatory process occurs, leading to the development of myelitis suppurativa, which is marked by softening and degeneration of the spinal cord tissue. Spinal cord infections can lead to serious consequences, such as:
- paralysis,
- neurological disorders,
- death.
The group of spinal cord infections includes:
- myelitis,
- epiduritis,
- spinal cord tissue abscess,
- meningitis and others.
Treatment in such cases includes restoring immunity and methods such as:
- antibiotic therapy,
- glucocorticoid therapy,
- anti-inflammatory therapy
- and detoxification.
Clinical manifestations of CNS infection
The clinical manifestations of CNS infection are very diverse, but common ones include:
- serious condition of patients,
- the presence of symptoms of general intoxication with hyperthermia,
- meningeal syndrome,
- as well as focal symptoms of brain damage in the form of loss of relevant functions.
Diagnostics
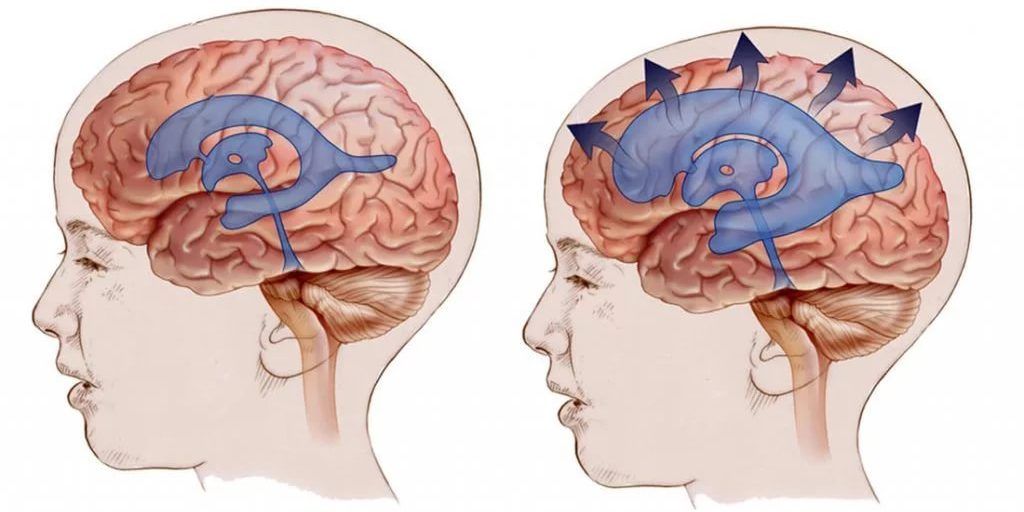
Diagnosis of infectious lesions of the CNS organs is based on characteristic clinical manifestations, data from blood tests, cerebrospinal fluid, and neuroimaging methods – MRI of the brain and spinal cord.
In most cases, treatment of CNS infections is carried out without surgery, however, in some cases, with a local accumulation of pus in the brain (abscess) or in the spinal canal, surgery is necessary to drain the purulent cavity or remove the entire formation.
Diagnosis of infectious brain lesions is based on clinical manifestations of infection, laboratory tests of blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and other biomaterials, such as saliva, urine, or oral cavity.
Clinical manifestations of brain infection may include headache, fatigue, fever, seizures, vomiting, and altered level of consciousness. Meningitis and encephalitis are the most common.
Laboratory tests may include determination of glucose levels, protein, red blood cells, white blood cells, and other components of the cerebrospinal fluid, reactions to viral and bacterial infections, antibody tests, and PCR to identify viruses and other microorganisms.
In addition, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is usually performed to determine the presence of signs of inflammation and restriction of fluid movement in the brain openings.
Depending on the diagnostic results, the doctor may recommend surgery to drain the cerebrospinal fluid or the introduction of antibiotics and antiviral medications to treat the infection.
Conservative treatment of infectious brain lesions
Infectious diseases of the CNS can be caused by:
- viruses (most often),
- bacteria,
- mushrooms,
- sometimes protozoa or parasites.
These diseases are accompanied by
- brain damage ,
- spinal cord
- and their shells .
The brain and spinal cord are normally protected from infection by the natural blood-brain barrier. However, if infection occurs, the consequences can be quite serious.
Encephalitis and meningitis
Inflammation of the brain is called encephalitis, and inflammation of the meninges is called meningitis. Often, bacterial inflammation of the meninges spreads to the brain itself, causing encephalitis.
Meningoencephalitis
Similarly, viral infections that cause encephalitis often also cause meningitis. If the brain and its coverings are infected, the condition is called meningoencephalitis.
Typically, in encephalitis and meningitis, the infection is not confined to one area. The inflammation can spread throughout the brain or its coverings. However, in some conditions, the infection is confined to one area in the form of a cavity or pocket of pus, called an empyema and an abscess.
Routes of infection
There are several ways in which the brain and its membranes can be infected. Bacteria and other infectious organisms can enter the central nervous system in several ways:
- hematogenous route (infection with blood flow),
- by contact – directly from the outside (for example, through skull fractures or during brain surgery),
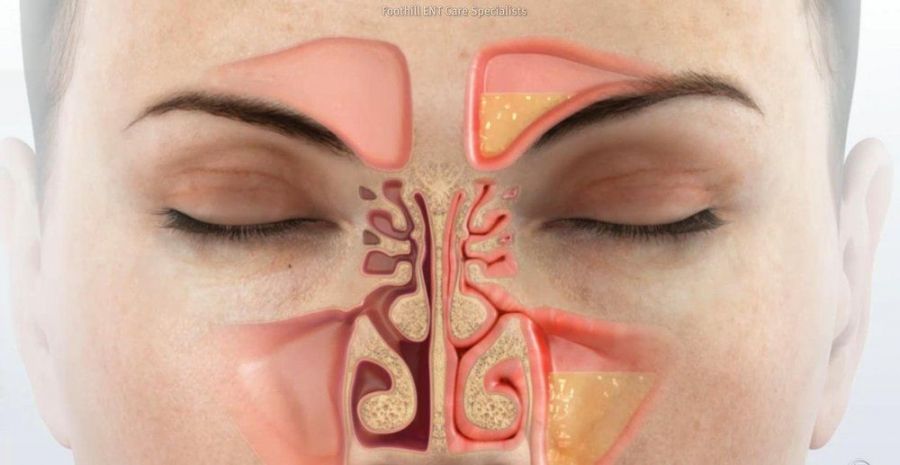
- with purulent inflammation of neighboring ENT organs (sinusitis, otitis media).
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment of infectious lesions of the CNS is a difficult task that requires a comprehensive approach.
Antibacterial therapy begins as early as possible, even before the results of bacteriological culture of infected material are available. As a rule, the most modern antibacterial and antiviral agents and their combinations are used. Most antibiotics penetrate the brain substance in insufficient quantities through the blood-brain barrier. Therefore, their intrathecal administration during spinal puncture is often used .
In particularly difficult cases, it is necessary to establish a long-term external spinal or ventricular drainage. In parallel with antibacterial therapy, active detoxification therapy and correction of immune disorders are carried out.
Surgical treatment of infectious brain lesions
Causes of brain damage
The most common causes of infectious lesions of the brain and spinal cord are:
Infectious complications of injuries
- skull base fractures ,
- penetrating head injuries ,
- firearms
- and mine and blast injuries.
Contagion
Due to the spread of infection from inflammatory foci, or as a result of iatrogenic causes:
- after punctures,
- blockade ,
- injections.
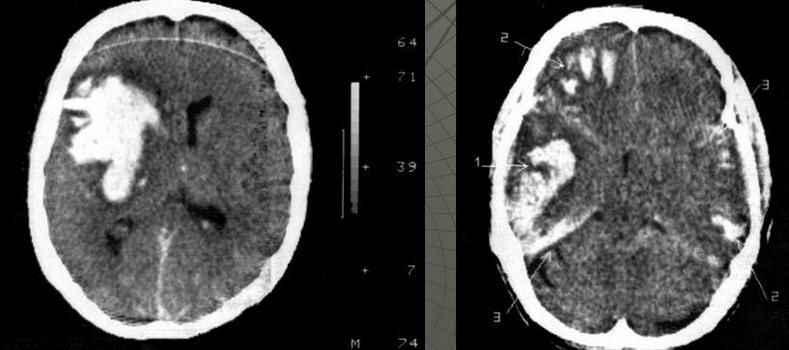
If the therapy is ineffective, abscesses – limited accumulations of purulent contents or empyemas – accumulations of purulent contents without clear boundaries – form in the cranial cavity and spinal canal.
Diagnostics
The most informative methods for diagnosing a purulent process are:
- MSCT
- and MRI with contrast.
Treatment of infectious lesions must be comprehensive, but if indicated, surgical intervention should be the primary treatment. Only after removal of the purulent focus does successful treatment of the patient become possible.
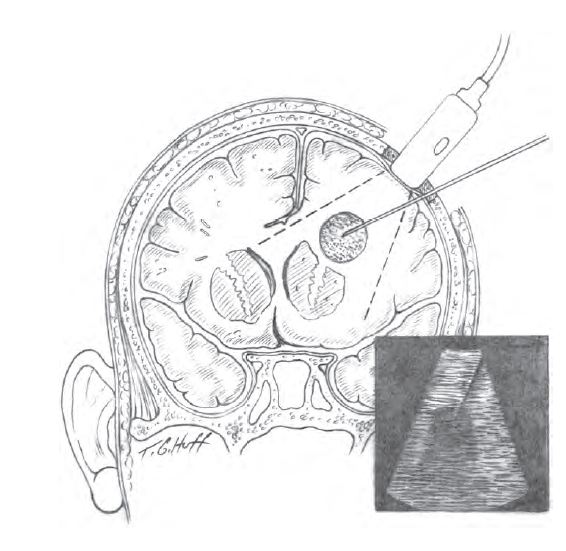
The main method of surgical treatment is drainage of the purulent focus: after careful planning of the surgical intervention, the patient undergoes a puncture of the accumulation of pus under general anesthesia, after which a drainage inflow and outflow system is installed in the cavity.
Through it, the remnants of purulent contents are washed out with antiseptic and antibiotic solutions for several days. During the operation, the contents of the abscess or empyema are taken for analysis in order to select the most effective antibiotic.
In the postoperative period, the patient undergoes MSCT to monitor the dynamics of purulent focus cleansing.
Sanitation
In the presence of a primary infectious process:
- otitis media,
- frontitis,
- odontogenic process
- etc.
It is imperative that its rehabilitation is carried out by a specialized specialist.
One of the latest techniques implemented in the neurosurgical department is the drainage of purulent processes in the brain under ultrasound navigation, which increases its accuracy and reduces traumatization of healthy tissues.
Neurosurgeon Malyshenko M.P.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 23.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: