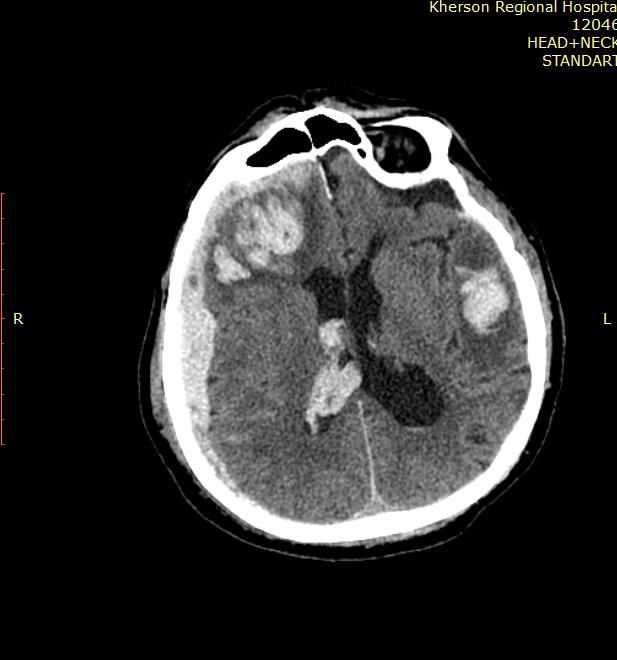
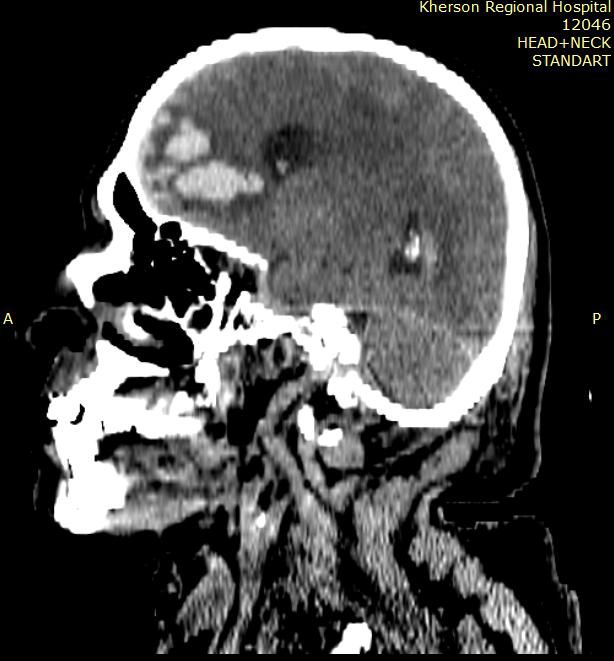
Diffuse axonal brain injury (DABI)
Diffuse axonal brain injury as a separate type of severe TBI was first described in 1956. DAP is manifested by a prolonged coma that occurs with TBI .
DAP is caused by diffusely extended axonal ruptures and small focal hemorrhages throughout the brain structures.
Usually damaged:
- brain stem,
- corpus callosum,
- white matter of the hemispheres
- and periventricular areas.
Events
Diffuse axonal brain injury (DABI) most often occurs in young adults and children. In childhood, it occurs with more severe neurological deficits.
Severity levels
Some authors propose dividing DAP by severity.
- A mild degree corresponds to a coma duration of 6-24 hours,
- moderate – coma lasting longer than a day, but without gross stem manifestations.
- Severe cases manifest as prolonged coma with symptoms of decortication and decerebration.
In any case, DAP is a serious condition with a high risk of transitioning into a vegetative state with subsequent lethal outcome.
That is why its effective treatment remains a relevant issue in practical traumatology and neurology.
Surgical treatment of severe bruising
Causes of severe injuries
Surgical treatment of severe brain injuries is indicated when compression-dislocation syndrome occurs, that is, when the brain is compressed.
The cause of compression-dislocation syndrome can be:
- hits,
- brain crushing,
- intracranial hematomas (intracerebral, epidural, subdural),
- Edema and swelling of the brain that do not respond to conservative (drug) therapy.
Treatment of severe injuries
All comatose patients have a sensor inserted through a small hole in the skull. The sensor can be placed in a ventricle of the brain, or in the brain tissue itself.
The sensor is connected to a monitor that measures intracranial pressure (ICP). If ICP increases, intensive therapy is performed to lower ICP, including draining cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain.
If these methods are ineffective, surgical treatment is performed with subtemporal decompression trepanation of the skull on both sides with a minimum size of 12×12 cm. In this way, the brain is freed from compression.
Craniotomy
In case of brain compression by intracerebral hematomas or foci of brain crushing, a trepanation of the skull of the required size is also performed. Then, through the brain tissue dissected in safe areas, the foci of damaged brain and hematomas are removed with a special micro-instrument.
Removal of subdural and epidural hematomas is described in other sections.
Conservative treatment of severe bruising
Conservative therapy
In case of severe brain injuries , if there is no compression-dislocation syndrome (brain compression), conservative therapy is performed.
Patients are treated in the intensive care unit. To ensure sufficient oxygenation of the brain, the patient is immediately transferred to mechanical ventilation (artificial lung ventilation).
Given the need for prolonged mechanical ventilation and adequate cleaning of the tracheobronchial tree, a tracheostomy is placed on the patient after 3-5 days. Mechanical ventilation is performed until the restoration of high-quality independent breathing.
If necessary, special mechanical ventilation modes are used, as well as modes with assisted breathing.
Great attention is paid to the patient’s nutrition. Both enteral (tube) and parenteral (introduction of nutrients into a vein) nutrition is provided. The issue of placing a microgastrostomy is resolved as early as possible, which prevents the development of infectious complications in the lungs.
The following are mandatory regulations:
- acid-base,
- water-electrolyte,
- protein balance.
Antibacterial therapy is carried out taking into account regular cultures for flora (bacteria), and taking into account the bacterial background of the department.
Neuroprotective therapy is performed to normalize and restore brain functions.
Prevention
Prevention of bedsores is carried out using anti-bedsore mattresses. In addition, patients are turned frequently using the necessary positioning, and the skin is treated with special solutions and ointments.
To prevent the development of contractures (shortening of tendons), the following is performed:
- physical therapy,
- massage,
- physiotherapy procedures.
The prognosis is determined by the degree of brain damage, duration, and depth of the coma.
Mortality reaches up to 33%. If the patient remains in a coma for a long time, the prognosis is unfavorable.
Neurosurgeons Seledets O.A., Dmytruk V.S.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 22.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect:







