Types
Gunshot wounds can be:
- Non-penetrating damage to soft tissues and bone structures
- Penetrating head injuries (damage to soft tissues, bone structures of the skull, and brain).
Complaints
- headache ,
- dizziness,
- nausea,
- vomiting (often multiple),
- amnesia (memory impairment),
- presence of damage to the soft tissues of the head,
- hearing impairment,
- flushing of the face.
Complaints vary depending on the weapon used and the type of fragment that inflicted the wound, as well as the location and extent of the lesion, the type of entry channel, and associated intracranial injuries.
Head injury clinic
- Pancerebral symptoms:
- headache,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- dizziness,
- impaired consciousness)
- Trunk symptoms:
- floating eye movements,
- paresis (weakness in the limbs),
- bilateral miosis or mydriasis (dilation or constriction of the pupils),
- strabismus,
- swallowing disorders,
- Violation of vital functions (breathing, cardiac activity).
Focal symptoms
varies depending on the location of the injury:
- pupillary and oculomotor disorders,
- movement disorders,
- weakness in the limbs,
- lack of movement in the limbs,
- sensitivity disorders,
- speech disorders, etc.
Violation of vital functions
- bradycardia or tachycardia
- increased or decreased pulse rate, increased blood pressure,
- increased breathing rate.
Vegetative symptoms
- acrocyanosis (cyanosis of the fingertips, nose),
- hyperhidrosis (sweating) of the palms,
- “capillary play” (throws you into heat, then into cold),
- bradycardia, which later changes to tachycardia,
- fever,
- instability of blood pressure,
- tremor and others.
Diagnostics
- Skull radiography
- Puncture of the subarachnoid space with collection of cerebrospinal fluid for analysis.
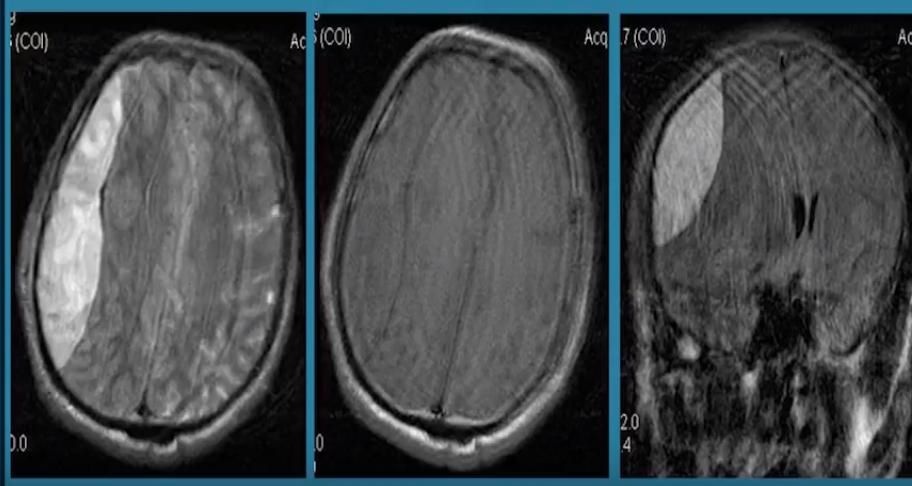
The leading diagnostic methods are computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
Craniograms allow to clarify the localization of defects of the skull bones and foreign metal objects, if any. Computed tomography allows to examine in more detail:
- origin of the injury,
- accurately indicate the presence and localization of hematomas,
- assess brain compression,
- the presence of a mass effect,
- distinguish gunshot and explosion head injuries from other types of injuries.
Surgical treatment of the head
All penetrating gunshot and explosive head injuries require early (up to 6 hours) primary surgical treatment (PST). PST for gunshot and explosive head injuries is performed in neurosurgical departments.
Neurosurgeon Dmytruk V.S.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 23.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: