Are you experiencing a sudden, unbearable headache? This could be a signal that you shouldn’t ignore. A brain aneurysm is a serious but treatable condition that everyone should know about.
Brain aneurysms: causes
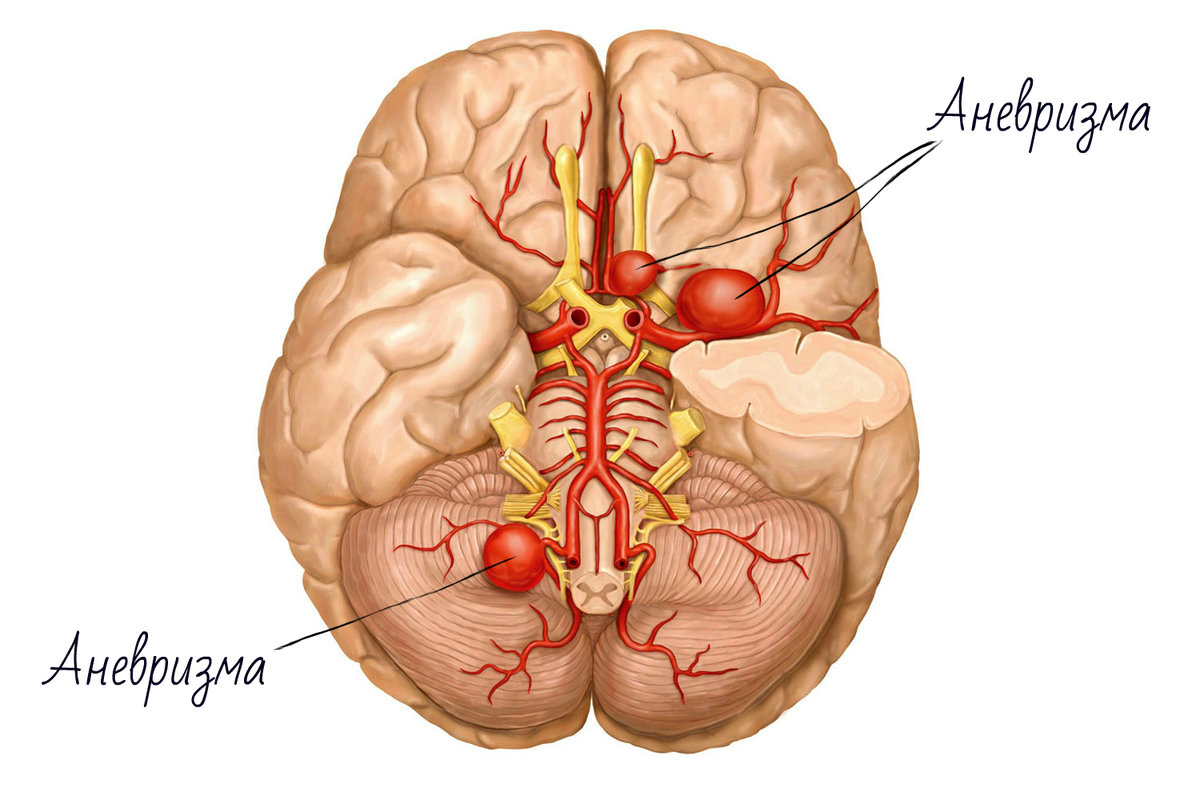
Cerebral artery aneurysms are one of the life-threatening causes of possible cerebral hemorrhage.
Aneurysms are bulges of thinned artery walls of various shapes and sizes.
Causes of thinning of the blood vessel wall:
- congenital factors (impaired embryonic vascularization)
- injuries
- infectious lesions of the arterial wall
Statistically, about 1% of the population has cerebral aneurysms. Over time, under the influence of blood pressure, there is a gradual increase in their size and thinning.
Symptoms and signs of a brain aneurysm
- increased blood pressure,
- stress,
- increase in intracranial pressure during tilts,
- physical activity,
- and sometimes, even in a state of complete well-being, a sudden rupture of the aneurysm occurs with cerebral hemorrhage,
- pain behind the eye or in the temple area,
- numbness of the face or part of it,
- double vision, blurred vision,
- disequilibrium.
This disease can be compared to a time bomb in the head, the rupture of which is unpredictable.
In most cases, cerebral aneurysms do not manifest themselves for a long time. Only a few days before rupture, a headache may be noted , and in some patients (with large aneurysms) neurological disorders may appear due to local pressure of the aneurysm on the nervous structures.
For example, when the oculomotor nerve is compressed, one eyelid droops and vision is impaired. A ruptured aneurysm is accompanied by severe headache, a feeling of “boiling water” in the head, impaired consciousness, nausea, and vomiting.
The headache does not go away for a long time, often moving to the back of the head and the back of the neck. Photophobia appears, the inability to tilt the head forward due to severe tension of the muscles of the back of the neck. If the volume of hemorrhage is minimal, these symptoms may regress independently, even without treatment.
Not to consult a doctor after such an “attack” would be a fatal mistake. Usually, after two weeks, the aneurysm ruptures again, which is fatal in 70-80% of cases. With massive hemorrhages, there is a loss of consciousness up to a deep coma with convulsions and respiratory failure.
Aneurysm risk factors
- high blood pressure,
- smoking,
- alcohol consumption,
- diabetes,
- taking medications that reduce blood clotting,
- hereditary predisposition (presence of aneurysms in relatives),
- head injuries,
- some congenital diseases (for example, polycystic kidney disease).
Diagnosis of aneurysms
Diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms, unfortunately, is most often carried out after their rupture. Sometimes aneurysms are detected in the “cold period” before rupture as an incidental finding during head tomography. The main diagnostic methods are:
- MSCT angiography,
- MRI angiography,
- and contrast cerebral angiography,
These methods allow you to detect a brain aneurysm and choose the optimal treatment tactics.
Modern methods of treating brain aneurysms
Treatment of cerebral aneurysms is only surgical, there is no conservative therapy. The purpose of the operation is to close the aneurysm, “exclude” it from the bloodstream. There are two methods of surgical treatment of cerebral aneurysms:
- Microsurgical clipping ,
- Endovascular embolization .
Frequently asked questions
What are the main symptoms of a brain aneurysm?
Often, an aneurysm is asymptomatic. If it is large, it may cause headaches, numbness, and vision problems. A ruptured aneurysm causes a sudden, extremely severe headache, nausea, vomiting, and loss of consciousness.
Why do aneurysms occur?
Most aneurysms are congenital. Other risk factors include hypertension (high blood pressure), smoking, head trauma, and hereditary predisposition.
What treatment is effective for aneurysm?
The only effective treatment is surgery. There are two main types of surgery: microsurgical clipping (an open procedure) and endovascular embolization (a less invasive procedure using a catheter).
Can aneurysm rupture be prevented?
It’s not always possible to completely prevent a rupture, but controlling your blood pressure, quitting smoking, and getting regular checkups, especially if you have a family history of aneurysms, can significantly reduce your risk.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 22.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: