Value
A subdural hematoma is a collection of blood that forms between the dura mater and the brain, the main cause of which is trauma. The main source of bleeding is damaged veins in the brain. A chronic hematoma is one that occurs more than 14 days after a traumatic brain injury.
The main feature that distinguishes an acute subdural hematoma from a chronic one is the presence of a connective tissue capsule that forms 2 weeks after TBI and separates the hematoma from the brain.
In most cases, patients do not seek medical help and can walk with this problem for several months or even years. Sometimes even minor blows to the skull can lead to these problems, and only at the height of clinical symptoms do patients seek medical help.
Symptoms
- headache (which is most often of a “bursting” nature),
- dizziness, nausea, vomiting,
- speech impairment (the patient cannot say a word and/or does not understand the meaning of what is said),
- weakness in the limbs on the opposite side of the stroke
- epileptic seizures, mental disorders, memory impairment
- meningeal syndrome.
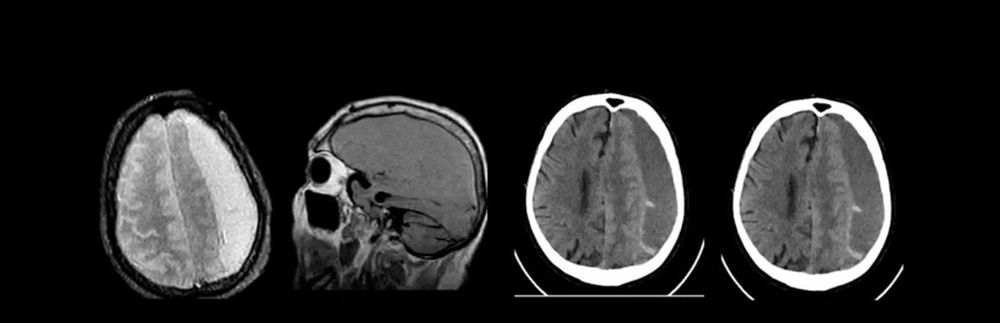
Diagnostic methods
ECHO-ES – in the absence of CT, MRI. The leading diagnostic methods are CT and MRI of the brain. Computed tomography is mainly performed in the acute period of injury because it better visualizes the accumulation of blood between the dural membrane and the brain.
In chronic subdural hematoma, MRI is preferred for diagnosis.
Indications for surgical treatment
- hematoma volume (according to neuroimaging data) over 50 ml in volume.
- dislocation of midbrain structures more than 5 mm
- deformation of the basal nuclei,
- hematoma volume (according to neuroimaging data) over 50 ml in volume.
- gross compression of the lateral ventricles with the development of hydrocephalus, regardless of size and localization.
Surgical treatment of subdural hematomas in most cases, if there are no partitions in the hematoma structure, is carried out through 2 small holes in the bones of the skull, through which tubes for the inflow and outflow system are inserted, through which the remains of the hematoma are washed out during the day, and the drains are removed 2-3 days after the operation.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 23.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect:








