When back pain becomes unbearable and every step brings discomfort, many questions arise: “What is happening to me?”, “Is it serious?”, “How to treat it?”. We understand your concern.
Spinal stenosis is a condition in which the space in your spine narrows, which can compress nerves and cause pain. It’s important to know that this is not a death sentence. In most cases, the problem can be resolved. Our goal is not just to relieve your pain, but to help you live a full, unrestricted life.
What is spinal stenosis: causes and types of the disease
Spinal stenosis (narrowing) is a chronic process in which the central spinal canal, lateral pocket, or intervertebral foramina become pathologically narrowed due to their compression by structures:
- bone,
- cartilaginous
- and soft tissue.
This leads to compression:
- spinal cord,
- nerve roots,
- vessels,
which are located inside the spinal canal.
Typical symptoms of spinal stenosis
- back pain;
- neurogenic intermittent claudication syndrome (the patient walks “from bench to bench”);
- radicular pain in the legs (one or both) (pulling pain in the legs, the pain intensifies when lifting the extended leg);
- weakness in the legs (one or both);
A characteristic symptom of spinal canal stenosis is intermittent claudication. Its presence allows us to assume that the patient has a narrowing of the intervertebral foramina even before additional examination methods are performed. The cause of intermittent claudication is most often instability in the lumbar spine (with instability, the vertebrae shift and further aggravate the stenosis).
How to recognize spinal stenosis: neurogenic claudication
- pain occurs when walking,
- regresses or disappears completely when squatting
- or tilting the torso forward.

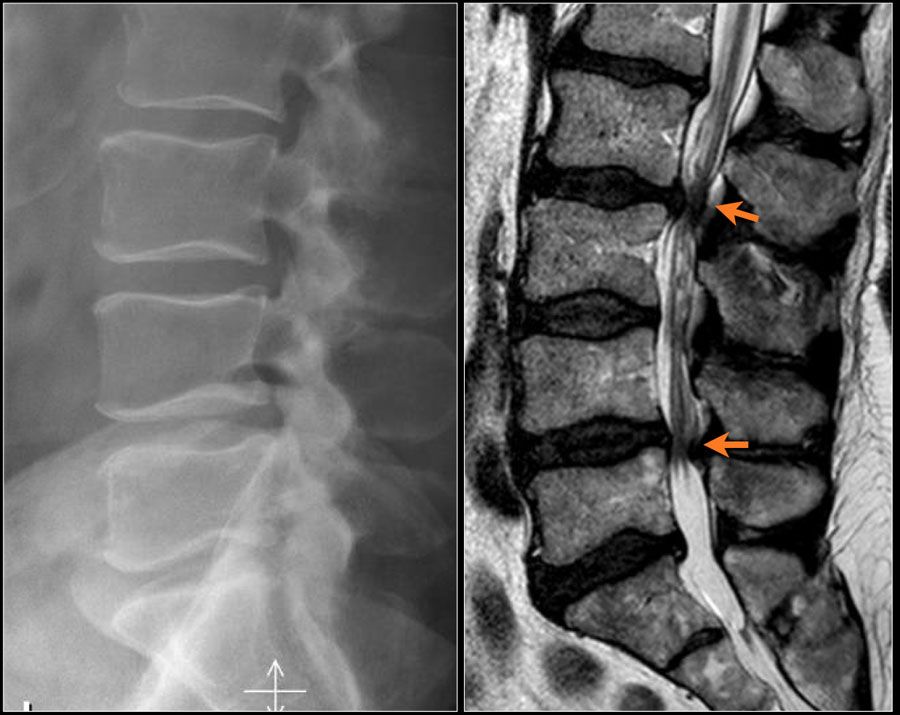
Modern diagnostics of stenosis: accurate examination methods
Spine X-ray
It is very important to perform functional radiography in degenerative diseases of the spine – during its performance, the patient should lean forward and backward as much as possible. If necessary, additional images are taken with tilts to the sides.
MSCT
Computed tomography clearly visualizes bone changes in the spine.
MRI
MRI is one of the most important examination methods. When performing MRI, soft tissue structures such as:
- hernias,
- protrusions,
- nerve roots,
- spinal cord.
Conservative treatment: when is surgery not necessary?
Reasons
This pathological condition can be either congenital or acquired during life. Congenital spinal stenosis is a genetically determined condition, inherited as a predisposition and manifesting at a younger age.
Acquired spinal stenosis is associated with the growth of the structures that form the spinal and root canals and usually results from:
- spinal diseases associated with age-related changes,
- various injuries,
- inflammation
- and other processes, some of which are also genetically determined.
The spinal canal consists of the following structures:
- brackets,
- spinous processes,
- articular processes,
- vertebral body,
- connections.
As shown in the figure, each of the structures can enlarge, causing narrowing of the vertebral canal or root canals and compressing nerve structures (spinal cord, roots).
Symptoms
The clinical picture develops depending on the compressed nerve structure. It usually includes a set of symptoms of damage to the corresponding part of the spine in the form of pain syndrome , which is aggravated in an upright position and with loads, inclinations, and in an anatomically unfavorable position.
Symptoms of nerve root or spinal cord damage also occur in the form of sharp or pulling pain radiating to the limb, numbness, and decreased strength in it.
Sometimes urinary or bowel disorders develop, such as incontinence or retention. The combination of motor disorders and bowel and bladder disorders are serious symptoms that indicate the need for urgent referral to a specialist .
The neurosurgical department employs specialists who are directly involved in the treatment of this type of pathology and know all the features of its clinical course and the subtleties of conservative and surgical treatment. By contacting us, you are entrusting your health to reliable and caring hands.
Treatment
The most common manifestation of spinal stenosis is intermittent claudication. In this case, the patient may walk some distance, after which he develops pain and weakness in the lower extremities, and is forced to sit or bend forward.
After some time, the symptoms subside and he can continue to move. The less distance a person can walk, the more pronounced the lameness. As a rule, the phenomena of intermittent lameness dominate over radicular symptoms.
Conservative therapy
Since spinal canal narrowing is an anatomical and permanent phenomenon, its successful conservative treatment is impossible. However, in case of refusal of surgery, conservative therapy of stenosis is performed, which includes:
- learning movements and poses,
- physical therapy,
- prescribing nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,
- epidural blocks with corticosteroids .
Calcitonin drugs play a certain positive role. Of course, conservative treatment of stenosis will not widen the spinal canal, but it can reduce swelling, inflammation, and other manifestations, leading to a temporary improvement in well-being.
At the current stage, it is believed that patients with a small number of symptoms in the initial stages of the disease can be treated conservatively. If the symptoms are many or severe, then surgical treatment is preferred.
Surgical treatment of stenosis: minimal trauma and rapid recovery
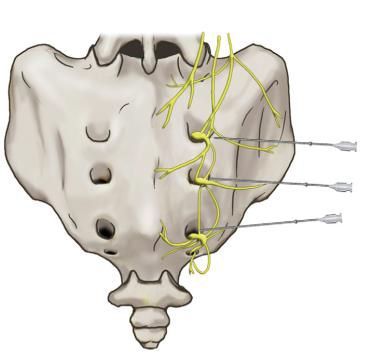
Epidural block
Under X-ray guidance, a special needle is inserted into the epidural space (the space between the dura mater and the inner wall of the vertebra). A pharmacological composition consisting of an anesthetic and a hormone is injected through this needle.
These blockades allow to reduce swelling, inflammation in the area of compressed nerve structures. The pain passes. Improvement occurs immediately. The duration of the procedure does not exceed 20-30 minutes. The effectiveness in the short term is very high.
Unfortunately, after a few months the effect decreases significantly and a repeat procedure may be required.
Laser vaporization of the disk
In combination with spiral nucleotomy, it is performed if spinal canal stenosis is caused by a bulging or herniated disc .
Under X-ray control, a special needle is inserted into the intervertebral disc. Through this needle, a special spiral-type instrument is inserted, on which the disc tissues are wound and pulled out in parts. After that, a laser fiber is inserted through the same needle and the disc is “vaporized”.
As a result of the operation, the volume of the disc decreases, the stenosis of the spinal canal is eliminated. The pain disappears. The duration of the operation is up to 30 minutes, local anesthesia.
Microlaminectomy
It is performed if spinal canal stenosis is caused by pathological growth of the vertebral arches.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia. A small incision of up to 4 cm is made. Then, using special microinstruments, a part of the enlarged vertebral arch is resected (removed) under a microscope.
As a result of the operation, the stenosis is eliminated, the nerve structures are released. The pain goes away. The duration of the operation is up to 1 hour.
Microforaminotomy
It is performed if spinal canal stenosis is caused by pathological growths of the vertebral bones and soft tissue components in the area of the intervertebral foramen.
Through a small incision, special micro-instruments are used under a microscope to remove these components, which eliminates compression of the nerve structures.
The pain goes away. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The operation lasts up to 2 hours.
Can surgery be avoided?
This is one of the most common questions, and the answer depends on your specific case. If the disease is detected early, conservative treatment is often sufficient to help control symptoms. However, if the stenosis progresses and your quality of life is significantly impaired, minimally invasive surgery may be the best solution.
My goal is to always start with the least invasive methods. We will discuss all the options in detail and together we will choose the path that is best for you. Don’t let fear stop you from living your life to the fullest.
Neurosurgeons Leontiev O.Yu. and Nazarenko O.S.
Frequently asked questions about spinal stenosis
What symptoms indicate spinal stenosis?
The most characteristic symptom is neurogenic claudication, which is characterized by pain or weakness in the legs when walking. Symptoms usually disappear when the person sits down or leans forward. Numbness, tingling, and back pain may also occur.
Can spinal stenosis be cured without surgery?
In the early stages of stenosis, conservative treatment is possible, including medications (anti-inflammatory drugs), physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises and epidural blocks. These methods help relieve pain, but do not eliminate the cause of the narrowing of the canal. In case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be required.
What modern methods of surgical treatment of stenosis exist?
Modern surgical techniques are minimally invasive. These include microlaminectomy and microforaminotomy. These operations are performed through small incisions, allow for rapid nerve compression relief, and significantly reduce recovery time.
When is it necessary to consult a neurosurgeon?
You should make an appointment with a neurosurgeon if you experience persistent back pain that radiates into your legs, weakness or numbness in your extremities, or if the pain limits your ability to walk the usual distances. Don’t delay, as early diagnosis and treatment greatly increase your chances of a successful recovery.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 22.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: