Fractures of the skull and frontal sinuses
In case of a traumatic brain injury with the application of impact force to the bones of the skull, fractures can quite often occur – both the vault and the base of the skull.
Types of fractures
- linear,
- fragmentary,
- perforated,
- pressed.
Fractures occur when bone fragments are pressed into the cranial cavity. In this regard, they are divided into:
- Impressional, when the anatomical connection of the fragments with the adjacent bones of the skull is preserved,
- Depressive – when the anatomical connection is lost.
Degrees of debris displacement
In addition, compression fractures differ in the degree of displacement of fragments into the cranial cavity.
More than the thickness of the broken bone
If the displacement into the cranial cavity is greater than the thickness of the broken bone, this leads to:
- compression of the brain tissues located below ,
- injury or compression of nearby blood vessels, which causes the development of those
- or other neurological symptoms.
Sometimes a brain contusion zone forms under the fracture site . In addition, it must be taken into account that the meninges are located under the bones of the skull.
Skin damage
If the skin and adjacent soft tissues over the broken bone are damaged, then such a craniocerebral injury with a fracture is considered open and therefore there is a risk of infection entering the cranial cavity .
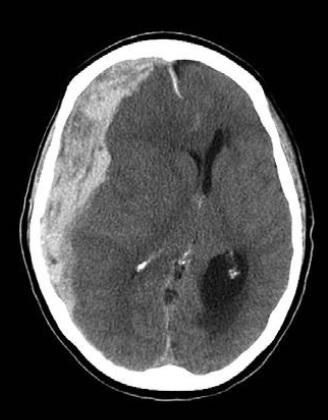
Damaged dura mater
If the dura mater is damaged and a clear fluid called cerebrospinal fluid, which normally bathes the brain and spinal cord, leaks through the wound (or natural openings), then such a head injury is considered open and penetrating. In this case, surgical treatment is usually necessary.
Diagnostics
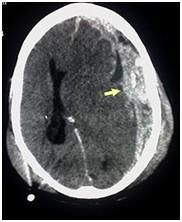
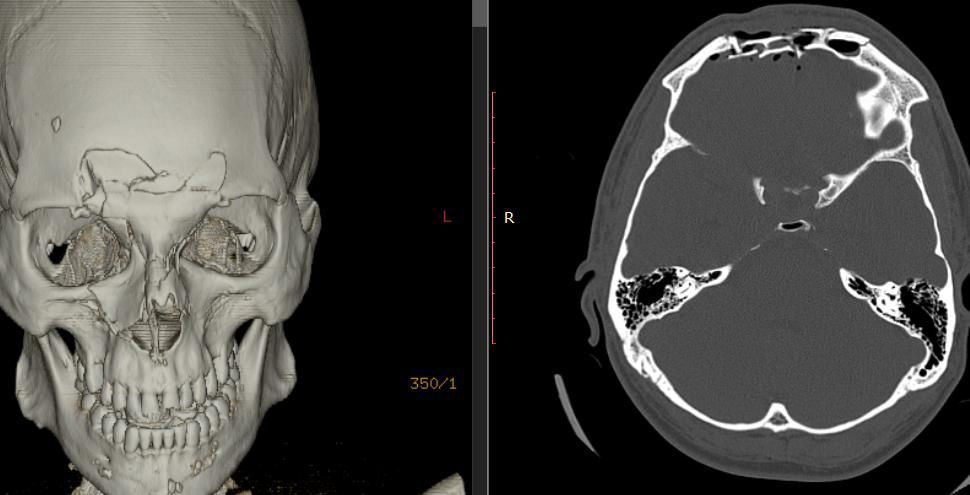
A compression fracture can be detected during surgical treatment of the wound, using X-rays of the skull bones, and is best diagnosed when performing a computed tomography scan of the head.
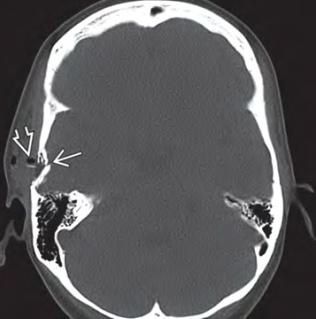
Surgical treatment
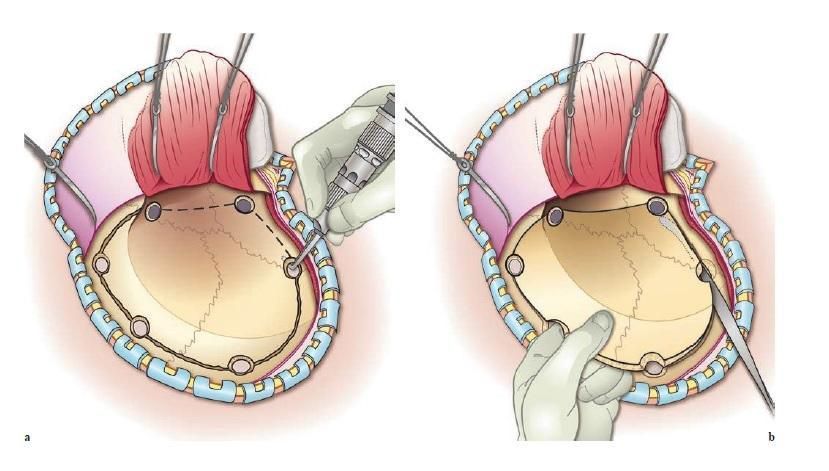
Compressed fractures of the skull bones usually require surgical neurosurgical treatment.
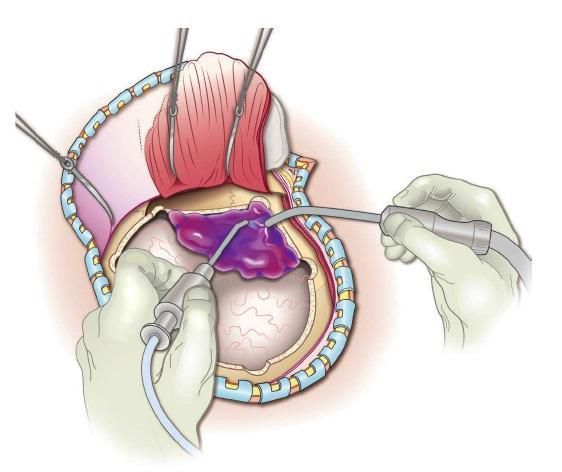
During the operation, the impacted fragments, if possible, are raised to their normal anatomical level, after which they are fixed to the surrounding bones using special titanium implants, screws, and special medical cement.
If the dura mater is damaged , it must be carefully sutured or hermetically sealed with natural tissues or special materials.
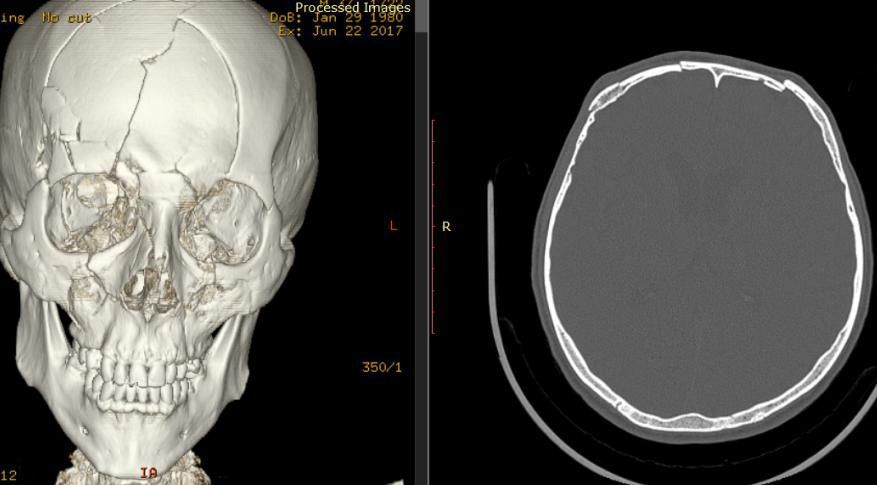
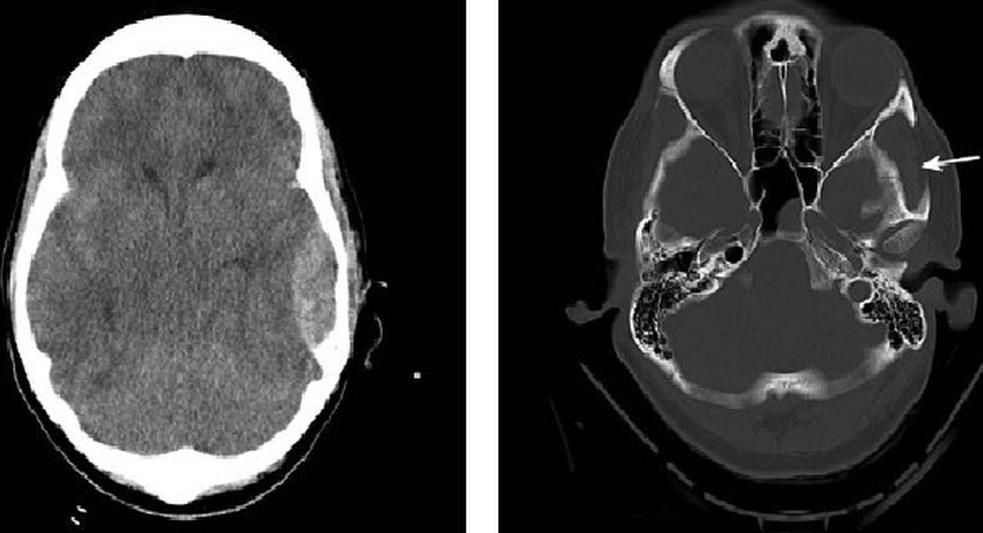
Compressed fractures of the frontal sinus walls
Sometimes, with traumatic injuries to the frontal bone, a so-called compression fracture of the outer and/or inner walls of the frontal (frontal) sinus may occur.
It is located in the eyebrow area, is an air-filled sinus, its walls are quite thin and break quite easily, which manifests itself as a rather noticeable depression in the injured area, which is perceived as a serious cosmetic defect.
Feature of the frontal sinus
It is because it is an air-bearing cavity, has an anatomical connection with other paranasal sinuses, and may contain pathogenic (disease-causing) bacteria that can cause infectious complications in the area of the depressed fracture, which, in turn, can lead to the development of intracranial infection.
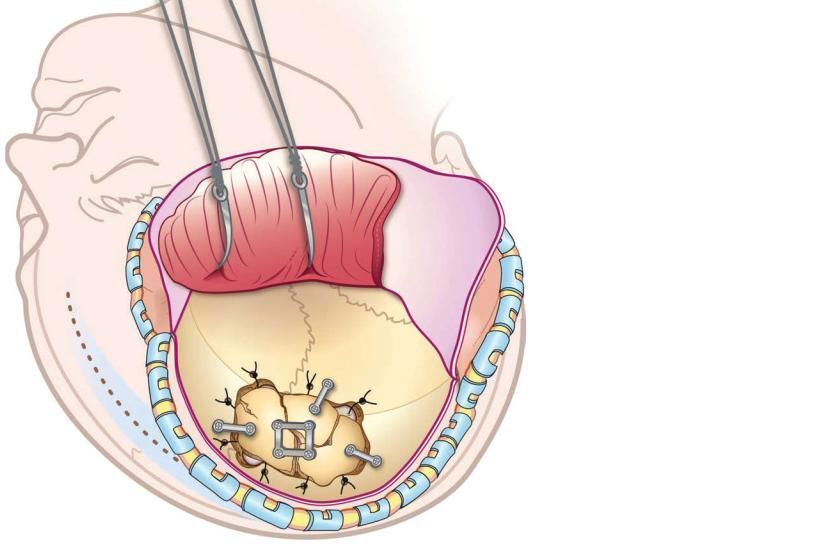
Surgical intervention
In addition, it is important that surgery be performed as early as possible to prevent the possibility of improper fusion of the pressed bone fragments.
During the operation, the bone fragments of the depressed fracture are set in place, after which they are fixed with titanium implants and screws.
If the posterior wall of the frontal sinus is damaged, there is a fairly high probability that the meninges are also damaged, which can lead to cerebrospinal fluid leakage from the fracture area.
Then it is necessary to carefully sew up the damaged dura mater or perform hermetic plastic surgery with natural tissues or special materials.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment of compression fractures is performed if:
- the displacement of fragments into the cranial cavity does not reach the thickness of the bone,
- absence of neurological symptoms,
- no signs of brain compression,
- in case of patient refusal of surgical treatment.
Special attention in the course of conservative therapy is paid to the prevention of intracranial infectious complications.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 22.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect:







