What is spinal deformity?
Spinal deformity is a disruption of the normal anatomical structure of the spinal column that can affect functionality and cause painful symptoms, mobility problems, and other complications. The deformity can be congenital or acquired, and its forms are diverse.
Acquired spinal deformity develops due to
- injuries,
- inflammatory processes,
- infections,
- degenerative diseases
- or chronic incorrect body position.
It is often accompanied by pain, limited mobility, and requires a comprehensive approach to treatment, which may include drug therapy, physiotherapy, orthopedic methods, and sometimes surgery.
In cases of severe deformities, surgical correction may be used, which allows restoring the correct position of the spine and improving the patient’s quality of life.
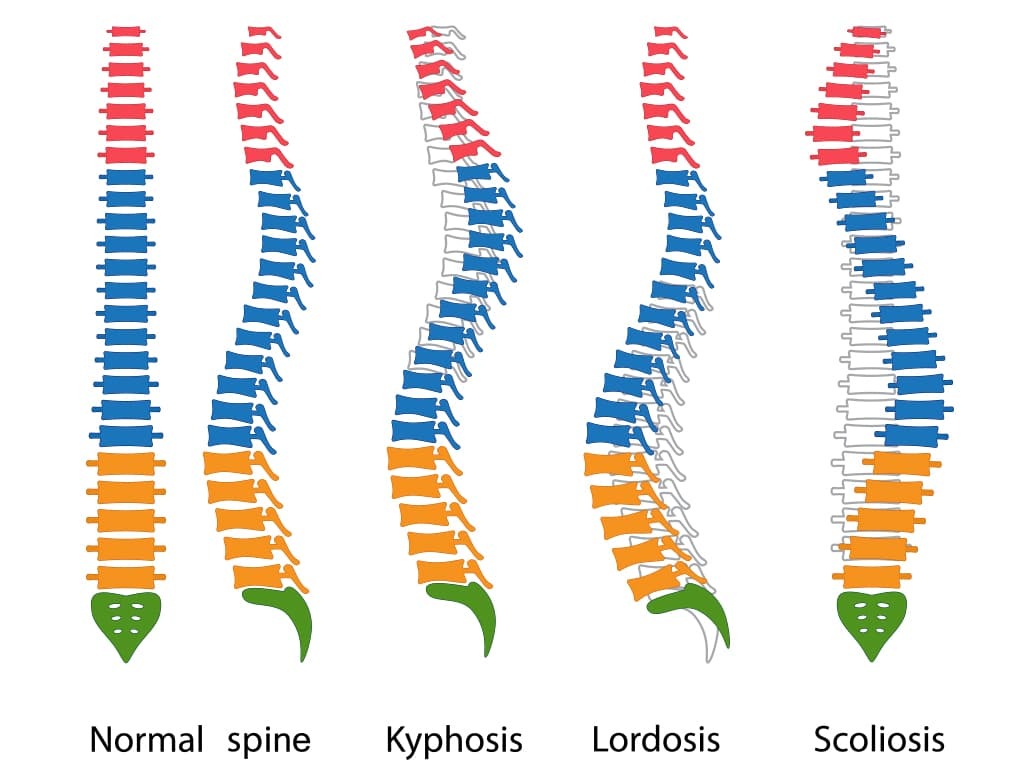
Types of spinal deformities
Various types of spinal deformities belong to degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine , such as:
- Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine that leads to body asymmetry and can disrupt the functions of internal organs.
- Hyperlordosis is an excessive forward curvature of the spine, usually in the lumbar region, which can cause pain, muscle tension, and pelvic organ dysfunction.
- Kyphosis is an excessive posterior curvature of the spine, among which there are congenital, acquired, as well as postoperative and post-traumatic forms.
Kyphotic spinal deformity
It is characterized by excessive curvature of the spine backward, resulting in the thoracic spine being shaped like a hump. It can be caused by degenerative changes, injuries, chronic diseases, or incorrect body position. In severe cases, this deformity causes pain, limited mobility, and affects the functioning of internal organs, especially the lungs.
Scoliotic spinal deformity
This is a sideways curvature of the spine that can occur in any region, but most often affects the thoracic and lumbar spine. Scoliosis can have varying degrees of severity and lead to body asymmetry, pain, dysfunction of internal organs, including the heart and lungs, as well as psychological problems due to aesthetic changes.
Treatment of spinal deformities
Treatment methods include:
- Conservative treatment — drug therapy, physiotherapy, and exercise therapy aimed at reducing pain and improving mobility.
- Traction and corset therapy — the use of spinal traction methods and wearing corsets to support and correct the position of the spinal column.
- Decompressive-stabilizing and reconstructive interventions are surgical operations aimed at relieving pressure on nerve structures (decompression) and restoring spinal stability using special constructs.
Conservative treatment of spinal deformities
When a patient presents with back pain, a neurosurgeon will always order an additional examination – magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This method is the most informative in diagnosing degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine, unlike computed tomography, which is an X-ray examination and visualizes only bone structures.
MRI reveals:
- protrusions
- herniated discs
- tumor-like formations
- intervertebral joint cysts
- etc.
If the patient develops neurological disorders such as:
- weakness
- loss of sensation in one or both legs
- pelvic organ dysfunction
- severe pain syndrome that is not relieved by analgesics
- detection of the substrate on MRI (most often a herniated disc with sequestration)
– the patient is shown surgical intervention.
With mild neurological disorders, such as:
- impaired sensitivity in the leg
- periodic pain syndrome that does not require pain relief
- detection of small median hernias on MRI
– the patient is offered conservative treatment.
In order for the prescribed treatment to be most effective, the patient is hospitalized in the neurosurgical department of the Kherson Regional Clinical Hospital.
The prescribed treatment complex must include:
- painkillers,
- muscle relaxants,
- drugs that improve the conductivity and trophism of nervous tissue.
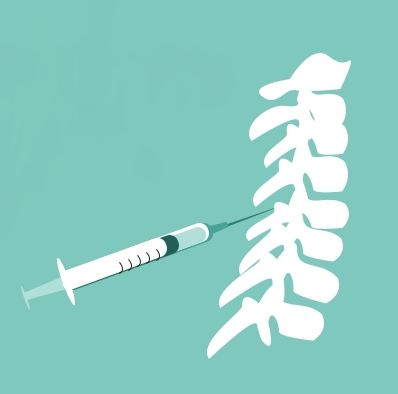
Also, a mandatory procedure is a blockade, thanks to which analgesic, anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory drugs are delivered directly to the site of the affected nerve root and are highly effective even with severe pain syndrome.
Conservative treatment: exercise therapy
The complex of conservative treatment is supplemented by physiotherapy and therapeutic exercise. The presence of a qualified exercise therapy specialist in the department allows each patient to individually select a set of exercises that will strengthen the muscular corset and will not harm the compromised spine. The patient will also receive recommendations on lifestyle and physical activity after discharge from the department.
If additional factors that can provoke pain syndrome are detected in the patient, the necessary interventions are performed to eliminate them. In particular, pain can occur when trigger points are irritated (their blockade or radiofrequency denervation is performed ), with pathology of the intervertebral joints (blockade of the facet joints is performed).
The neurosurgeon has extensive experience in the treatment of vertebrogenic pain syndrome. All procedures, manipulations and surgical interventions are performed only according to indications.
Frequently asked questions about spinal deformity
What is spinal deformity?
What should not be done with scoliosis?
What is scoliotic deformity?
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 22.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: