Spinal cord injury
This is an injury characterized by damage to the substance of the spinal cord, resulting in organic damage to neural structures along with functional disorders.
As a result of the injury, neuroimaging shows hemorrhages (hematomyelia), areas of crushing, edema, and partial or complete rupture of the spinal cord.
Damage can be both primary, that is, occurring at the time of injury, and secondary, resulting from impaired blood supply in the post-traumatic period.
Sometimes this type of injury carries infectious complications, especially when it is an open injury. In the acute period, spinal cord contusion often manifests itself with symptoms of complete or partial conduction disturbance.
Clinical picture
which can be used to assess the extent of the damage is not formed immediately, but over a certain period after the injury. It varies from slight weakness in the limbs to complete paralysis. Sensory disorders below the level of injury can sometimes reach complete anesthesia.
Pelvic organ dysfunction manifests itself in the form of urinary and fecal incontinence or retention.
With a complete rupture of the spinal cord, concomitant pathologies such as infectious complications, congestive pneumonia, and pressure sores develop very quickly, against the background of constant bed rest.
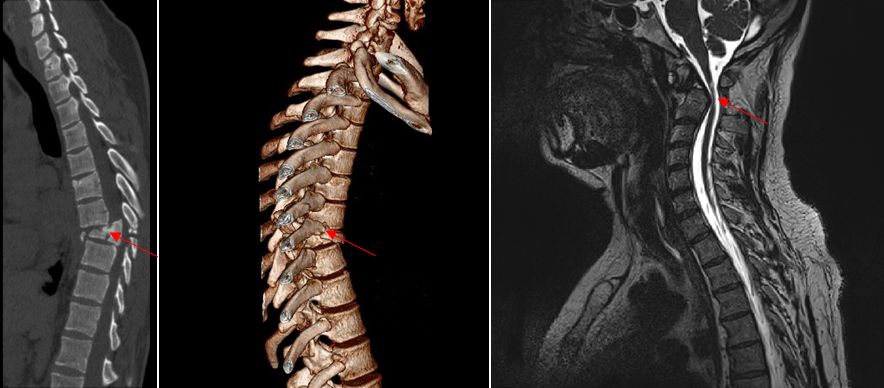
Diagnostics
CT and MRI are the gold standard for diagnosing spinal injury.
Lumbar puncture is a laboratory diagnostic method that detects hidden blood in the cerebrospinal fluid and is performed in the absence of CT and MRI.
Treatment
The treatment is mainly surgical, the goal of which is to decompress the spinal cord. If there are no indications for surgical treatment, spinal cord contusion is treated conservatively with the appointment of:
- anti-edematous,
- metabolic,
- vascular
- and pain relief therapy.
The goal of this treatment is to improve metabolism and conduction in nervous tissue.
As part of conservative treatment, the patient is early activated, in which the patient is taught to move independently. This reduces the likelihood of various complications.
Exercise therapy
Also, elements of therapeutic physical education are such as:
- breathing exercises,
- different types of massage,
- acupuncture methods,
- magnetotherapy,
- electrical stimulation ,
- UHF amplipulse,
- electro- and phonophoresis,
- various blockades (paravertebral, epidural, transforaminal),
are extremely important treatment methods for patients with spinal cord injury.
Forecast
Often, when conducting comprehensive conservative therapy in patients with spinal cord injury, it is possible to restore neurological functions, which allows achieving both social and professional adaptation after the end of rehabilitation measures.
Spinal cord concussion
This is the mildest form of traumatic injury to the nervous system, which is characterized by reversible functional and neurological disorders within a period of a minute to several days, against the background of conservative therapy.
The main differential sign of this type of injury is that when performing computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, there is no evidence of organic damage to the spinal cord.
Clinic
- decreased muscle strength in the limbs
- impaired sensitivity and reflex activity.
- urination and defecation disorders (most often this is urinary retention).
All symptoms completely regress within the first day.
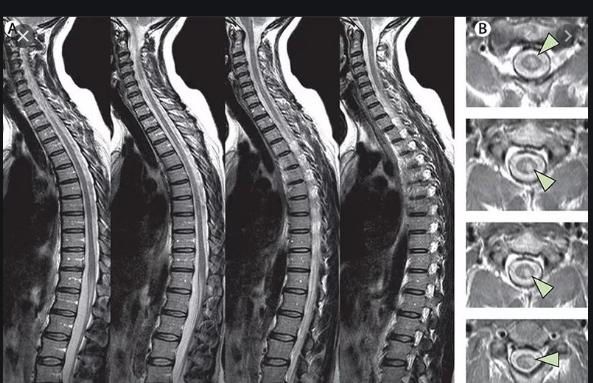
Diagnostics
The gold standard in diagnosing spinal cord concussion is CT and MRI, which show no organic lesions of the spinal cord and neurovascular structures of the spinal canal. In addition, there is laboratory diagnostics, the main method of which is the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid for occult blood.
Treatment
is mainly symptomatic, and as a rule it is aimed at analgesic, vascular and metabolic therapy aimed at restoring conduction in the spinal cord, after which the patient recovers. In addition, physiotherapy and rehabilitation are included in the complex treatment.
Recommendations and further treatment
Patients are recommended bed rest with limited physical activity and a gradual increase in motor activity. Further treatment is carried out by a neurologist at the place of residence.
Conservative and surgical treatment of concussion and contusion
Surgical treatment of the lesion
Indications for surgical treatment of blunt spinal cord injury :
- compression of the spinal cord and its roots by hematomas ,
- fragments of vertebrae,
- foreign bodies,
- spinal canal deformation (according to CT, MRI scans, post-traumatic spinal instability, blockage of cerebrospinal fluid outflow pathways, post-traumatic liquorrhea, progression of sensory and motor disorders, dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Early decompression (removal of compression of neural structures) with spinal stabilization , the beginning of rehabilitation measures from the moment the patient is admitted to the hospital, and timely and appropriate pharmacotherapy are the key to successful treatment of patients with this type of traumatic injury.
Decompressive and stabilizing surgery
Based on this, in this situation, it is most appropriate for a neurosurgeon to help the patient with a combined surgical intervention – a decompression-stabilization operation, which involves decompression (elimination of compression of nervous structures by a pathological substrate) and stabilization of the spinal column to restore its axis and biomechanics, and therefore, normalize its physiological functions.
During reconstructive decompression-stabilization operations, the curvature of the spine, its instability, is eliminated, the spinal canal is expanded. During decompression, only those tissues that directly compress the nerve structures are removed. In some cases, various types of implants ( cages ) are installed between the vertebral bodies (the so-called PLIF technique, with fixation of adjacent vertebrae with titanium screws and beams).
Transpedicular spinal stabilization
Transpedicular spinal stabilization – during this surgical intervention, screws are inserted into the vertebral bodies through the root of the arches using special instruments, which, together with titanium beams, eliminate pathological deformation of the vertebrae when the system is fully installed.
At the necessary moments (when screws are inserted near the spinal cord), the necessary X-ray image of the spine is obtained. Such control allows minimizing the risk and reducing the duration of the operation.
Specially designed minimally invasive systems allow surgeons to install screws and rods that create a supporting “framework” for the affected parts of the spine through several small (up to 1.5 cm) skin incisions, rather than making a large and deep “half-back” wound for the necessary access to the spine.
The installation of these systems also does not take place “blindly”, but under dosed X-ray control at any stage of the operation. The undoubted advantages of this technique are its low-traumatic nature, cosmetic appearance, reduced blood loss during the operation and its shortened duration.
In this case, the patient is usually lifted to his feet the next day after the operation. The course of inpatient treatment of neurosurgical patients with spinal cord injury is 20-30 days, with further continuation in outpatient conditions or, in the absence of contraindications, in sanatorium-resort medical institutions.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 22.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect:








