Ischemic stroke
About 140 thousand new cases of ischemic stroke are registered in Ukraine annually. In the Kherson region – 2700.
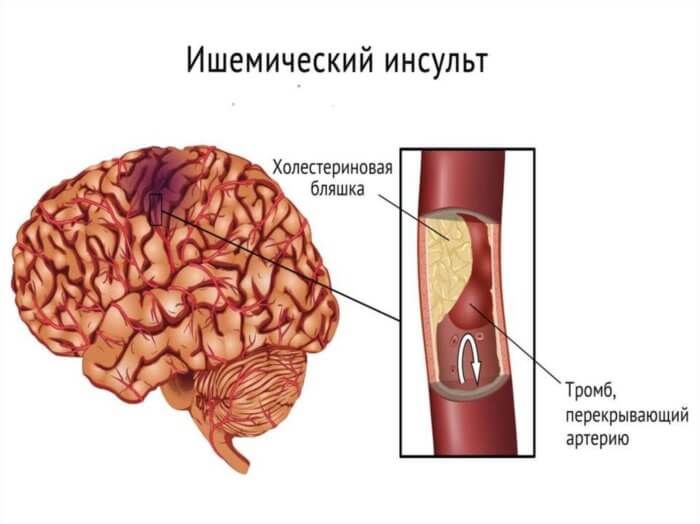
Atherosclerosis of blood vessels leads to the deposition of cholesterol plaques, which significantly narrow the lumen of the carotid arteries and impair blood supply to the brain.
This causes the development of repeated ischemic strokes and progressive degradation of memory and higher mental functions.
Symptoms of acute ischemic stroke
- speech impairment,
- severe weakness in the left or right limbs,
- pronounced coordination disorders with nausea and vomiting,
- blindness in one eye that occurs acutely.
Harbingers of stroke
Terrifying precursors of stroke that often go unnoticed:
- periodic headache,
- dizziness,
- increased blood pressure after the age of 50,
- memory loss,
- periodic vision disorders,
- coordination disorders.
These are all initial signs of a vascular catastrophe – ischemic stroke of the brain. All patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension are in the “risk group.”
To diagnose this pathology, a method available to everyone is used – duplex ultrasound of the neck vessels. It allows you to detect atherosclerotic plaques in the carotid arteries in the early stages. In case of pronounced narrowing, surgery is required – stenting of the carotid arteries or removal of plaques (endarterectomy).
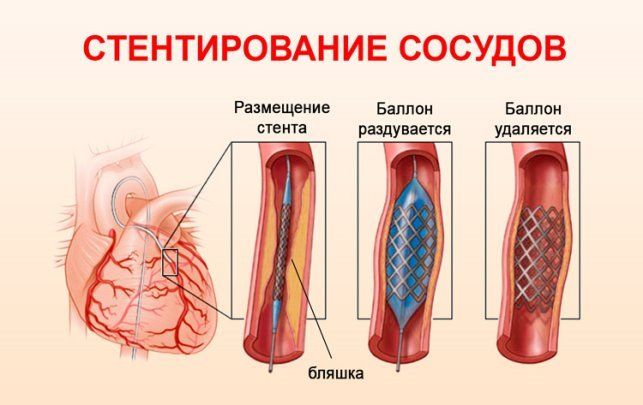
Carotid artery stenting
This is a minimally invasive surgery aimed at removing the narrowing of the artery and restoring normal blood supply to the brain. Arterial stenting is performed under local anesthesia through a single puncture of the skin and artery. A special instrument is inserted through the lumen of the vessel to the site of arterial stenosis and a stent (a metal mesh “spring”) is installed, which widens the narrowed area of the vessel and strengthens its wall.
Removal of atherosclerotic plaque from the carotid artery (endarterectomy)
Features. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Through a cosmetic incision in the skin on the neck, the carotid artery is isolated at the point of its branching. The vessel is cut, the atherosclerotic plaque is removed, and a vascular suture is applied.
The total duration of the operation is about 40 minutes. During the operation, the carotid artery above and below the incision site is clamped with special clamps. As a result of the operation, the lumen of the vessel is completely restored, eliminating the risk of further strokes.
Hemorrhagic stroke
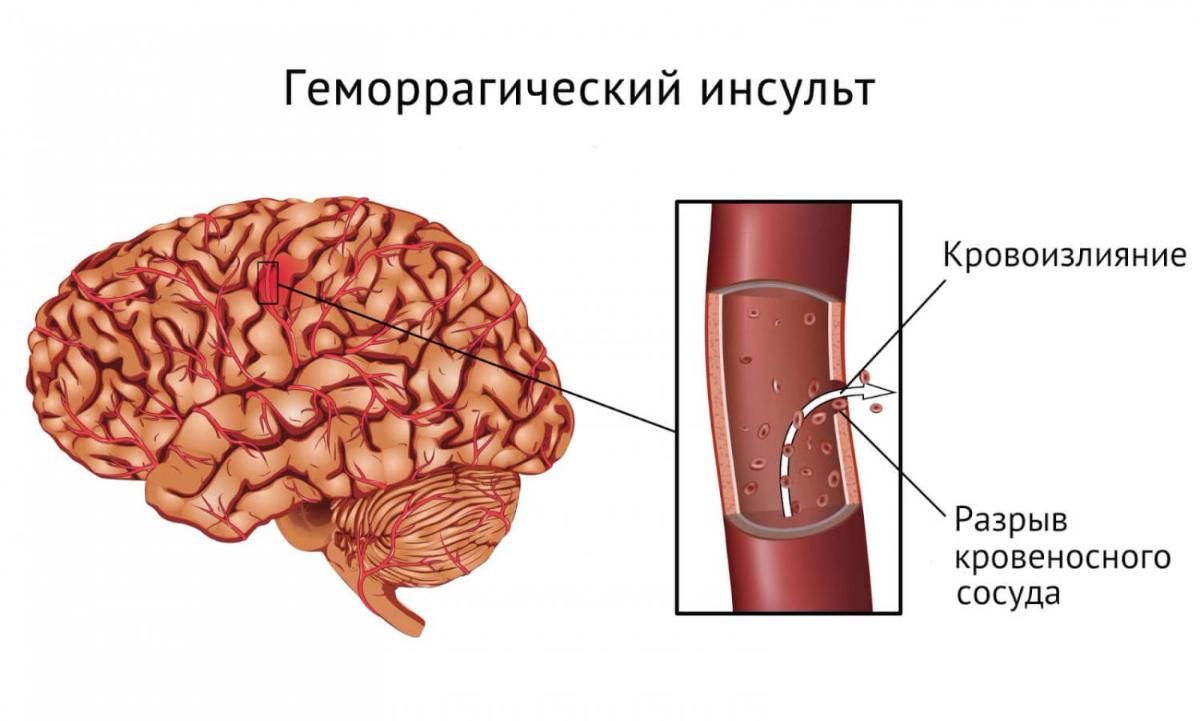
Cerebral aneurysm is a disease in which a section of the wall of a cerebral vessel bulges outward, gradually “bloating.” As a result, the delicate vascular wall can rupture both under physical and emotional stress, high blood pressure, and with normal blood pressure.
An aneurysm may not cause any symptoms until it ruptures . Sometimes it can press on the oculomotor nerve, causing double vision or drooping eyelids.
Symptoms of a ruptured cerebral aneurysm
- severe headache,
- feeling of “boiling water pouring into the head”,
- loss of consciousness,
- cramps.
The severity of the condition after a ruptured aneurysm depends on the volume of hemorrhage. If it is minimal, then even the headache may not be pronounced. With massive hemorrhages – 50% of patients die immediately.
Those patients who have survived a hemorrhage and are in stable condition require urgent surgery due to the risk of rebleeding, which is usually much more massive than the initial one. The operation consists in “eliminating” the bleeding aneurysm.
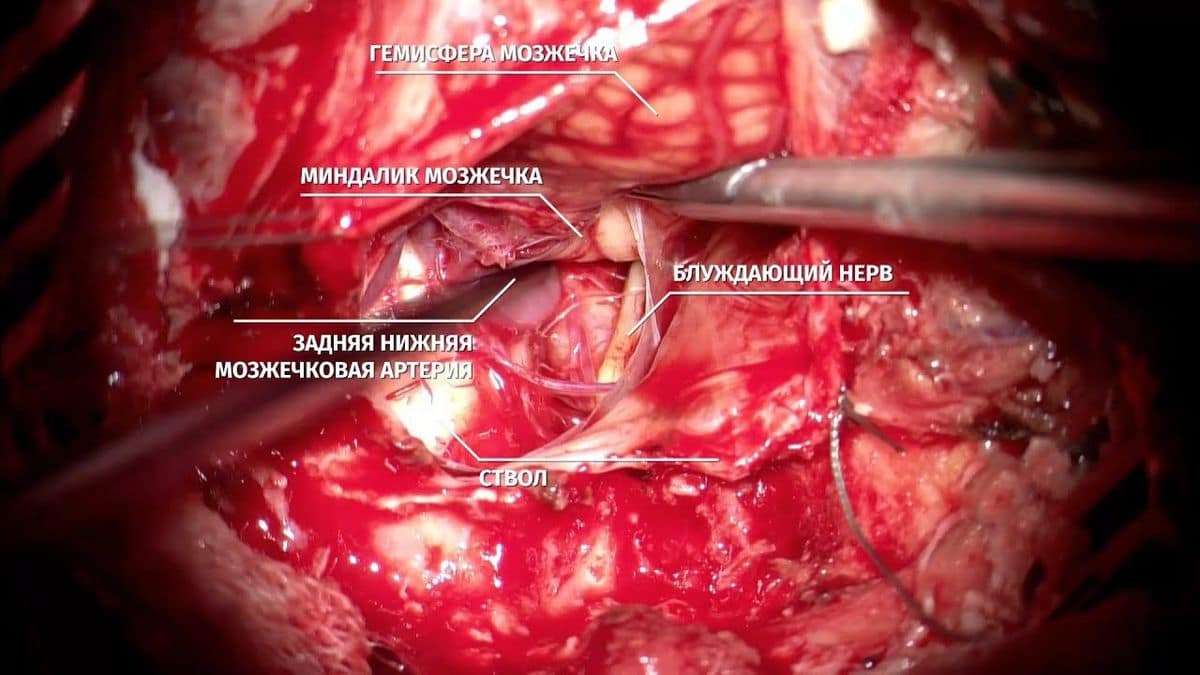
Microsurgical clipping
The operation for clipping an aneurysm is performed under general anesthesia using an operating microscope and microsurgical equipment. After a small trepanation of the skull, the cerebral vessel with the aneurysm is isolated, after which a special titanium clip is placed on its neck. The hemorrhage that occurred when the aneurysm ruptured is also removed.
Diagnostics
Before surgery, in order to clarify the diagnosis, diagnostics are performed:
- MSCT with contrast
- or cerebral angiography.
These studies can also be performed after surgery for postoperative monitoring.
Sometimes, after a hemorrhage, surgery is required to create bypasses for the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid ( shunt surgery ).
Endovascular embolization
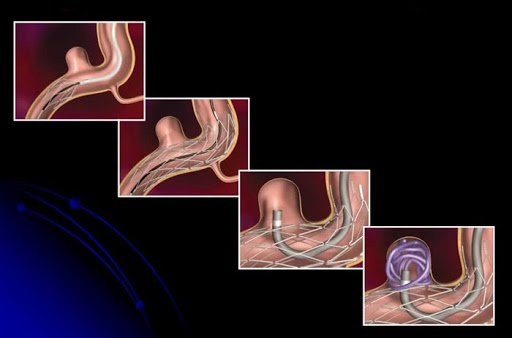
Endovascular embolization is a minimally invasive surgical treatment for cerebral aneurysms. This procedure does not require craniotomy.
The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia through a single puncture of an artery in the leg, through which a thin tube-catheter is inserted into the artery and guided through the aorta and neck vessels into the vessels of the brain to the location of the aneurysm.
Through the specified tube, special metal endovascular microcoils with “shape memory” are introduced into the lumen of the aneurysm, which twist into a ball in the aneurysm cavity. This leads to a complete stop of blood flow in the aneurysm, which makes it impossible for it to rupture again.
This operation is performed under constant X-ray control.
Sources of information
The information in this article is based on data from leading medical organizations and scientific studies:
- Center for Public Health of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine (CPH): Official statistics and epidemiological data on ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes in Ukraine.
- World Stroke Organization: International guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of stroke, including endovascular techniques.
- American Heart Association/American Stroke Association: Clinical protocols and recommendations for carotid stenting, aneurysm embolization, and other surgical procedures.
- Scientific medical publications: Information about the symptoms and mechanisms of stroke development is based on modern research published in peer-reviewed scientific journals.
Стаття написана: 27.05.2020
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 23.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect:







