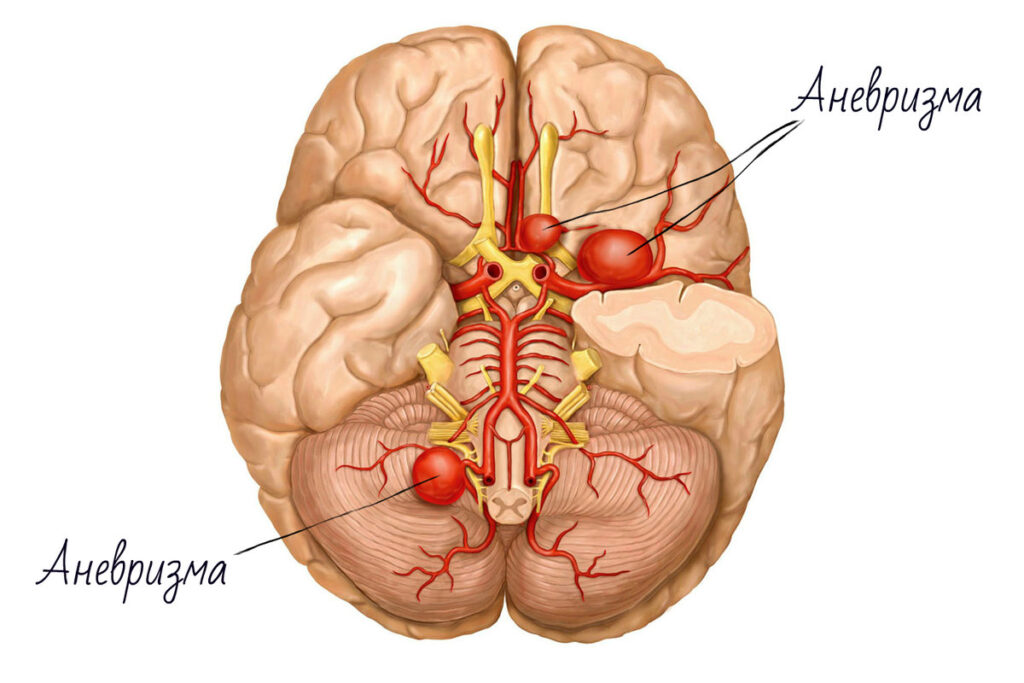
Cerebral angiography (CAG)
Among many modern methods, CAH has remained the “gold standard” for diagnosing vascular pathology of the brain and neck for 90 years worldwide.
Method
The method of angiography of cerebral vessels consists of injecting an iodine-containing, radiopaque substance directly into them, which sequentially fills first the large arteries, then the smaller arterioles, capillaries, and finally the veins.
During the injection of contrast, serial X-rays are taken on a digital X-ray angiograph, which is an electron-optical converter with a powerful computer. This allows you to obtain high-quality images of the vessels, see the entire anatomical picture of the vascular basin, and also assess the dynamics of blood flow.
Thus, the uniqueness of direct cerebral angiography lies in the possibility of comprehensive assessment of the anatomy and function of the vascular bed in real time. The recorded images can be viewed repeatedly frame by frame, which provides important information for the diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases.

Diagnostics
Cerebral angiography is used to diagnose:
- cerebral aneurysm ,
- arteriovenous malformations ,
- stenosis of arteries and veins,
- congenital anomalies of the vascular bed,
- diagnosis of stroke causes,
- assessment of the functional state of cerebral blood flow.
CAG, unlike MRI and MSCT, is an invasive examination method that is performed in an X-ray operating room. Under local anesthesia (if necessary with intravenous sedation), a puncture of a large artery is performed (usually the femoral artery in the groin area).
A thin catheter is inserted through the puncture hole, which is guided through the vessels under X-ray control and inserted sequentially into the carotid and vertebral arteries in the neck, which supply blood to the brain.
The manipulation itself is painless. During the injection of the contrast agent, a feeling of warmth in the head, a metallic taste in the mouth, a feeling of “flashes or lightning” in the eye may occur. After the examination, a load is applied to the site of arterial puncture , and strict bed rest is required for 6 hours to prevent bleeding from the site of arterial puncture and the formation of a subcutaneous hematoma.
MSCT angiography
MSCT-angiography allows you to obtain a digital three-dimensional image of the vessels of the head and neck in a few minutes, built on the basis of thin slices of X-ray tomography with contrast enhancement. Such an image allows you to assess the location of the vessels relative to the structures of the brain and the base of the skull, which is very important for further surgical tactics. MSCT-AG of the brain is of particular value in acute intracranial hemorrhages. The sensitivity of this method is up to 97%. Contraindications to this method of examination are allergic reactions to iodine-containing contrast, impaired renal function.
MRI angiography
The method of magnetic resonance angiography is based on the effect of a high-power magnetic field on the tissues of the body, the degree of change of which is perceived by special detectors and, thanks to computer data processing, a three-dimensional image is constructed.
Our hospital uses a modern tomograph with a magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla to obtain MRI images.
Performing an MRI of the brain takes much longer (from 20 to 40 minutes), so it is extremely difficult to perform it on patients in serious condition. The sensitivity of this method is high and reaches 99%.
In most cases, contrast is not required to obtain images of blood vessels during MRI angiography, so this method can be used in patients with impaired kidney function and allergies to iodinated contrast agents. Contraindications to this method include metal implants and pacemakers.
Ultrasound duplex scanning of the neck arteries
Ultrasound of the neck vessels is a simple and reliable non-invasive method for diagnosing vascular diseases. A special ultrasound sensor is used to obtain the image. This method has no contraindications, because it does not use contrast agents or X-rays.
Duplex scanning allows you to detect vascular diseases that can lead to stroke in the early stages.
Advantages
The high resolution of the sensors allows you to detect:
- narrowing of the carotid and vertebral arteries,
- measure the degree of narrowing,
- blood flow rate,
- determine the anatomical features of arteries and veins,
- the presence of bends,
- tortuosity of the arteries.
The most valuable information is the structure and density of the atherosclerotic plaque that causes the narrowing of the artery. This information cannot be obtained by other research methods.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 22.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: