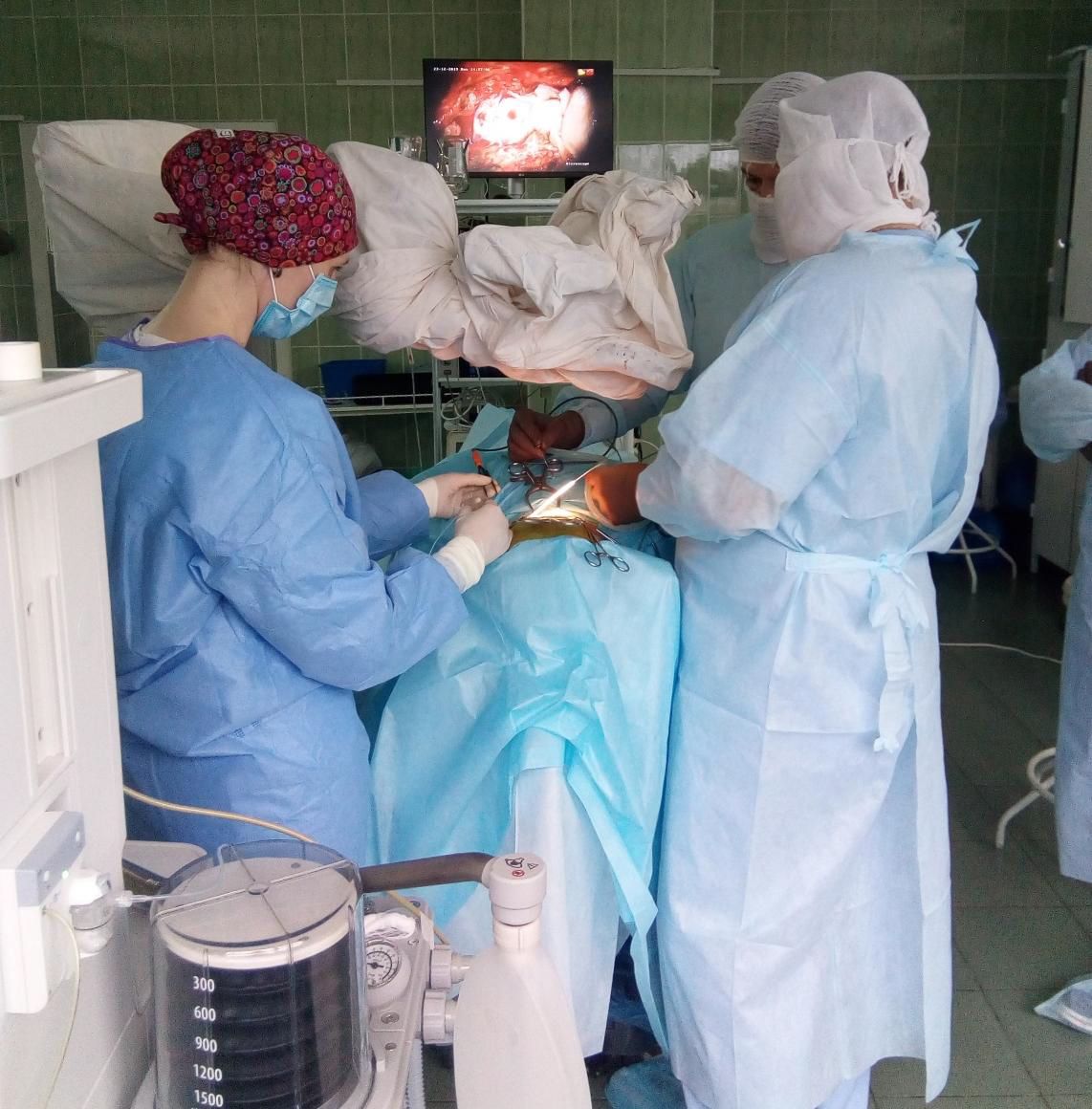
Neurosurgical treatment
After neurosurgical treatment of injuries and diseases of the nervous system, the patient often requires a fairly long and comprehensive rehabilitation treatment, which is aimed at returning the person to an active full-fledged life and professional activity, or at adapting to a persistent health disorder (disability) with the most complete social readaptation.
Types of rehabilitation treatment
- Drug treatment
- physical therapy
- different types of massage
- physiotherapy
I would like to give a few examples of the most common consequences of neurosurgical diseases and injuries.
Trepanned Skull Syndrome
It develops in patients with skull bone defects after surgery, which is usually performed for traumatic brain injury, vascular or oncological pathology of the brain. This syndrome is manifested by a headache, which is often associated with changes in weather conditions:
- atmospheric pressure,
- ambient temperature,
- as well as protrusion of the contents of the skull under the skin in the area of the defect during coughing, sneezing, tilting the head, or physical exertion.
In addition, patients complain of fear of brain damage due to the “bone window”, as well as a cosmetic defect.
Given the post-traumatic impairment of cognitive mental functions (encephalopathy), difficulties arise:
- in focusing attention,
- performing intellectual tasks,
- memory impairment,
- sleep,
- decreased resistance to emotional stress and alcohol.
Sometimes seizures can develop in the presence of provoking factors.
Cranioplasty
Cranioplasty is a method of surgically reconstructing the bones of the skull after injury or surgery.
The operation allows you to perform:
- correction of a cosmetic defect,
- eliminate the risk of brain injury due to a bone defect,
- prevents the formation of scar adhesions in this area.
A wide variety of materials are used for cranioplasty (the patient’s own bone, metal and acrylic implants, bone cement, etc.).
Chronic subdural hematomas
Chronic subdural hematoma is a collection of blood between the dura mater and the brain substance that occurs as a result of head injury.
Even seemingly minor trauma sometimes leads to damage to the venous vessels of the brain, especially in the elderly.
Chronic subdural hematomas include those that occur 14 days or more after the injury, when a capsule of connective tissue has already formed around the hematoma. As a rule, in most cases, the patient is unaware of the presence of an intracranial hematoma and can “walk” with it for several months or even years.
When the condition decompensates, symptoms such as a throbbing headache , dizziness, nausea and vomiting, impaired attention, movement, and mental function develop.
In most cases, our department performs removal of chronic subdural hematoma in a minimally invasive manner – through 2 small holes in the bones of the skull, with subsequent drainage of the hematoma cavity within 24 hours.
Post-traumatic and degenerative spinal deformities
In post-traumatic spinal deformities, as well as in degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis and spondylosis), complications often arise in the form of:
- herniated intervertebral discs ,
- scoliosis (curvature of the spine),
- stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal,
- spondylolisthesis (“slipping” of vertebrae from each other),
- the appearance of spinal instability.
This leads to a disruption of the normal anatomy of the spinal canal, which affects the nerve structures located in it – the spinal cord and its roots, which, in turn, leads to the appearance of neurological deficits in the form of impaired movement, sensitivity, and functions of the pelvic organs.
In this situation, it is most appropriate for the neurosurgeon to help the patient with a combined surgical intervention:
- decompressive-stabilizing reconstructive surgery on the spine , which involves decompression (elimination of compression of nerve structures by a pathological substrate)
- and stabilization of the spine to restore its axis and biomechanics, and therefore, normalize its physiological functions.
Стаття написана: 22.01.2026
Стаття перевірена медичним спеціалістом: 23.01.2026
Popular destinations:
Advantages
When you consult a neurosurgeon, you can expect: